Jun 17, 2025
A pressure regulator is designed for systems where there is a risk of pressure fluctuations or where stable or zoned pressure control is required,it can also called pressure regulating valve which is primarily used to automatically regulate and stabilize the pressure of gases, liquids, and mixed media.
In most factories, compressed air is supplied by a centralized air compressor system. Due to the large number of user points throughout the system, pressure fluctuations are very common. Without a regulator, downstream equipment may malfunction or perform inconsistently due to excessive or insufficient pressure.
Certain equipment, such as painting robots and fixture control systems, require extremely precise pressure control— even a variation of just 0.1 bar can affect product quality. Therefore, pressure regulators are essential for accurate pressure adjustment and control.
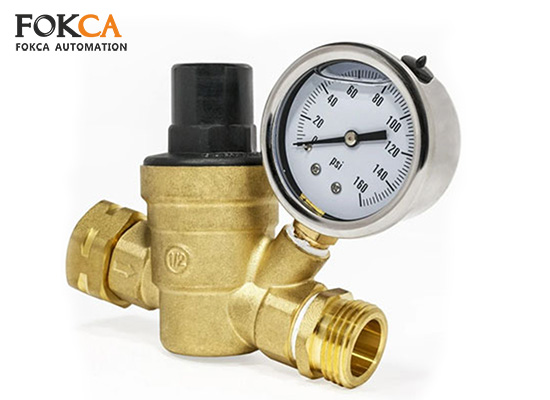

In industrial automation systems, pneumatic or hydraulic components are highly sensitive to pressure. Excessive pressure can lead to equipment damage, leaks, or even safety hazards, while insufficient pressure may cause actuators to malfunction, ultimately affecting production efficiency. Therefore, the pressure regulating valve is not merely an auxiliary component—it is a core safeguard for system stability, safety, and efficiency.It is a common fluid control component used to automatically adjust and stabilize the pressure of gases or liquids within a system to a set value.
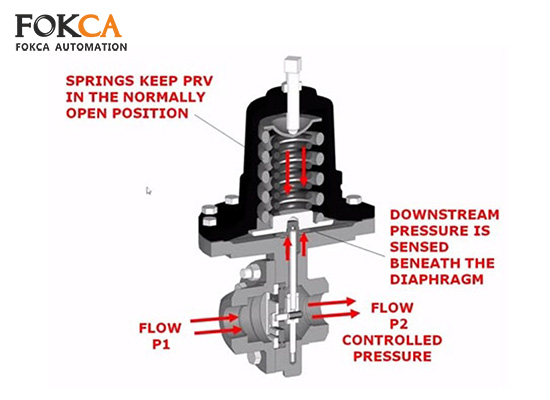
Before understanding how the pressure regulator valve works, it is necessary to first introduce the various components of the regulating valve.
Adjustment screw: Sets the target downstream pressure by compressing the internal spring.
Spring: Applies force to a diaphragm or piston to push the valve open.
Diaphragm or piston: Responds to downstream pressure changes.
Valve seat: Regulates the airflow or fluid flow through the valve.
At its core, a pressure valve works based on a feedback loop involving three main forces:
Spring force
Downstream pressure force
Valve plug force
You set the desired pressure by turning the adjustment screw. This compresses the spring.
The spring pushes the diaphragm down, opening the valve and allowing flow from the high-pressure side.
As downstream pressure builds, it pushes back on the diaphragm.
Once the downstream pressure equals the spring force, the valve reaches a balanced state and holds steady.
If downstream pressure drops, the spring force reopens the valve.
If downstream pressure increases above the setpoint, the diaphragm pushes the valve closed slightly.
You can also learn more about the various functions of Pressure Regulating Valve, its adaptability to different application industries, and installation methods.
Air Compressor Systems
Regulates output pressure to match downstream tool requirements, preventing damage from over-pressurization.
Air Source Treatment Units
Maintains steady pressure in pneumatic systems, ensuring reliable operation of air cylinders, actuators, and tools.
Fluid Transmission Lines
Controls pressure in water, steam, or chemical pipelines to protect equipment and maintain system stability.
Industrial Automation
Used to fine-tune pressure for different machines or zones, improving efficiency and protecting sensitive components.
Laboratory & Medical Devices
Ensures precise gas or fluid pressure control in sensitive systems like analyzers, respiratory devices, or lab instruments.

| Comparison Item | Pressure Regulating Valve | Pressure Relief Valve |
| Purpose | Actively controls,downstream pressure to a set value | Protects the system by releasing excess pressure |
| Operating Principle | Automatically adjusts valve opening to maintain pressure | Opens suddenly when preset pressure is exceeded |
| Installation Location | Typically installed between main supply and equipment | Often placed at pump outlets or end of pressure vessels |
| Common Applications | Air compressors, air preparation units, industrial automation | Hydraulic systems, boilers, water pipe overpressure protection |
While both valves can regulate system pressure, their control methods and purposes are different. A pressure relief valve is a passive regulator that protects the system, while a pressure regulating valve is an active control valve type that can be remotely controlled.
Although pressure regulators are very reliable in industrial applications,but sometimes they may still encounter some common issues that affect system stability and equipment lifespan.
◆ Unstable output pressure
◆ Stuck or sluggish valve response
◆ Failure to adjust, unable to reach set pressure
◆ Gas or liquid leakage
◆ Regular Inspections
◆ Regularly replace springs, diaphragms, and seals.
◆ Maintain a clean environment.
◆ Check filter function.
A pressure regulating valve is a control device that reduces and maintains fluid or air pressure at a desired level downstream, regardless of fluctuations upstream.
They work by using a spring-loaded diaphragm or piston to balance incoming pressure with a setpoint. As downstream pressure rises, the valve partially closes; as it drops, the valve opens more to maintain consistent output pressure.
Turn the adjustment screw or knob clockwise to increase the outlet pressure, or counterclockwise to decrease it. Always adjust while monitoring a pressure gauge on the outlet side.
Uncontrolled high pressure downstream
Insufficient or zero pressure
Pressure fluctuations or leaks
Install in the correct flow direction
Place it after a filter, but before sensitive equipment
Use Teflon tape for sealing threads
Include a pressure gauge for monitoring
Avoid installing upside down
You May Interest In


Jul 30, 2025 Blog
AWG:Why do We Need the American Wire Gauge?
Jul 28, 2025 Blog
How to check air solenoid valve?
Jul 24, 2025 Blog
How to check the solenoid valve?

Apr 22, 2025 Blog
Pneumatic Globe Control Valve
Apr 16, 2025 Blog
A Guide to Understand Angle Seat Valve
Apr 10, 2025 Blog
Limit Switches in Valve Control SystemsFOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap