May 27, 2025
Pneumatic solenoid valve is a kind of solenoid valve that controls the flow path of compressed air to drive Pneumatic actuators.It also can called air solenoid valve,receives commands from electromagnetic signals to control the on/off or directional switching of airflow Of compressed air, so it is widely used in various Pneumatic field that requiring to control compressed gass to actuate mechanical action.Industry is increasingly relying on automated production lines and intelligent control systems. With solenoid valves, the operation of pneumatic actuators will be more convenient, automated, and correspondingly faster.
Pneumatic solenoid valve with its fast response, simple structure, and high cost-effectiveness,is set to play an increasingly important role as pneumatic control systems become more widely used in the context of industrial automation and smart manufacturing.This article will make you learn more about working principle, control methods, advantages, and application guidance, helping you easily select the valve that best meets your needs. Let's embark on this journey of discovery together!
Why does the pneumatic actuator have high automation and remote control capabilities under the action of the pneumatic solenoid valve? The answers will be revealed one by one.
Air solenoid valve is explained a pneumatically operated control component that controls downstream pneumatic actuator through upstream electrical signals. Air solenoid valve features fast response, compact structure, high control precision, and easy integration into automated systems.
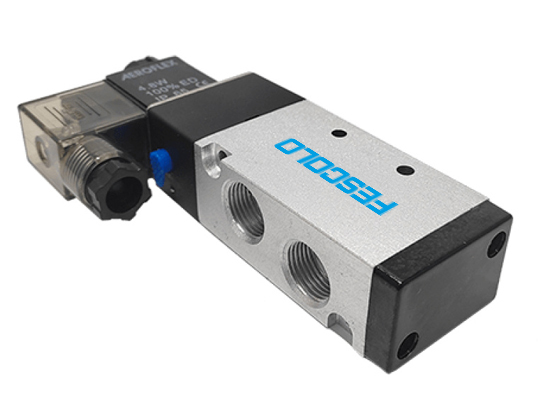

The main function of the air solenoid valve is to guide the action of the pneumatic actuator. After use, it will bring other functions to the system. Let's discuss them together.
◆ Airflow ON/OFF Control:When the solenoid coil is energized, it attracts the valve core to move, creating a passage for the fluid to flow through; when de-energized, it blocks the fluid flow.
◆ Directional Control:A pneumatic solenoid valve with multiple ports has a spool that shifts positions under the action of electromagnetic force and spring force. The compressed air is directed to different chambers of the actuator, enabling the piston rod to extend and retract.
◆ Remote & Automated Operation:The automation system sends an electrical signal from a distance to the coil of the pneumatic solenoid valve, generating a magnetic field that drives the valve spool.
◆ Failsafe Function:Its fail-safe function is achieved through a spring return structural design and auxiliary components, including a spring and dual solenoid coils.
The function of a pneumatic solenoid valve is to electrically control the on/off and direction of compressed airflow in a pneumatic system, Some types of pneumatic solenoid valve can be integrated with equipment for coordinated operation,which enables automated, accurate, and safe control of air-driven equipment.
Pneumatic solenoid valve has many types with different ways primarily affects their control method and circuit logic.
2-way control valve:The simplest pneumatic medium control,There is just an air inlet and an air outlet, mainly used to turn on or off the compressor airflow.
pneumatic 3-way solenoid valve:It has two position,one intake port, one exhaust port, and one exhaust port, commonly used for one-way control of cylinders.
5-way valve:Commonly used in double acting cylinder control, it has two position include intake port and exhaust port to achieve the control of the cylinder's telescopic action.
No matter how many ways in pneumatic solenoid valve, the flow of compressed air in the path and the action of the pneumatic cylinder are controlled by electromagnetic drive.
Air solenoid valve make the pneumatic actuator upgraded into an automated and intelligent motion unit. The use of the pneumatic solenoid valve brings a series of significant features and advantages to the pneumatic actuator.
◆ Significantly improve automation and remote control capabilities
◆ Increase response speed and frequency
◆ More precise control
◆ Increased safety and reliability
◆ Easier speed and force control
◆ Greater environmental adaptability
Under the control of the compressor air solenoid valve, the maintenance of the pneumatic actuator becomes more convenient, and the cost-effectiveness is significantly improved.

Automated Production Lines
Control the extension and retraction of cylinders to enable automatic grabbing, pushing, and transporting.Just like managing the end-effectors of robots for precise operations.
Packaging and Assembly Equipment
Operate compressed-air-driven devices such as grippers, cutters, and coding machines.Facilitate high speed and accurate sorting and packaging processes.
Food and Pharmaceutical Industries
Control pneumatic valves and conveyor equipment using clean, oil-free compressed air, meeting strict hygiene standards.
Medical Equipment
Used in precise pneumatic control systems in devices like ventilators and dental equipment to regulate small flow rates and high-frequency air changes.
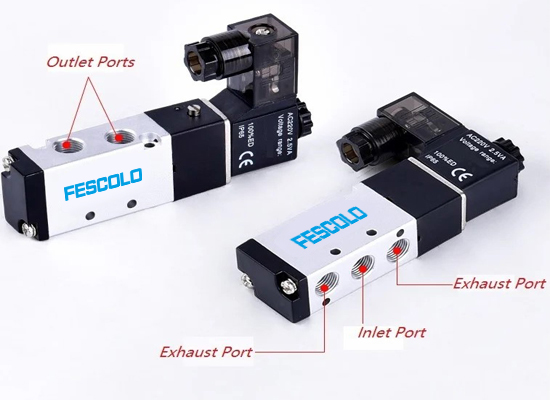

Air solenoid valve is mainly responsible for operating pneumatic actuators such as cylinders and other motion devices.
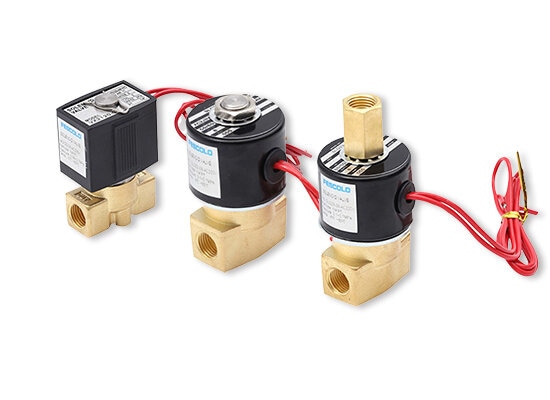
Air solenoid valve works from When the solenoid coil is energized, it generates a magnetic field that drives the valve core to control the on/off or directional switching of the compressor air, thereby enabling the opening, closing, or reversing of air operated actuators. When de-energized, it resets via a spring or air pressure.So pneumatic solenoid valve is widely used in various industries including automation equipment, machinery manufacturing, automotive, electronics assembly, food packaging, and medical devices.
The working of the solenoid valve is very simple. The following is the operation of each structural component.A solenoid pneumatic valve consists of following main parts to operate when working:
Plunger Movement: When the coil is energized, it creates a magnetic field that pulls the plunger, opening the air passage. To close the passage, the spring pushes the plunger back to its original position.
The coil or solenoid: which acts as a switch that converts electrical energy into magnetic energy.
The armature: which moves inside the valve chamber to direct the airflow.
The valve body: which controls the air flow through openings called ports.
A pneumatic solenoid valve is a type of remote active control valve, as it actively controls and regulates the on/off and directional switching of compressed air under the guidance of electrical signals, thereby driving the extension and retraction of pneumatic actuators.
Key parts of a air operated solenoid valve include Solenoid coil,Armature,Valve body,Spool,spring,Seals,Ports and Manual override.
The core feature of a pneumatic solenoid valve is its ability to remotely and automatically operate pneumatic actuators. Its working principle is that when the coil is energized, it drives the movement of the valve core, forming an air passage with the valve seat.
Fokca as a pneumatic solenoid valve manufacturers who uses high-quality stainless steel and advanced sealing materials to ensure each air solenoid valve offers exceptional pressure resistance and wear durability.We also have other types of valves, such as angle seat valves, globe valves, axial flow valves, check valves, and shuttle valves, which can be either automatic or mechanical.
Among the excellent products of peers,we supply products with advantages are Featuring energy-efficient coils and advanced pilot-operated control technology,which can achieve large flow control with minimal power usage. Contact us directly!
 Fluid Retention During Supply and Exhaust Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
Fluid Retention During Supply and Exhaust Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
 Pressure Fluctuation During Flow Path Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
Pressure Fluctuation During Flow Path Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
 Control Characteristics of 2-Way Solenoid Valves in Intermittent Liquid Supply Systems
Control Characteristics of 2-Way Solenoid Valves in Intermittent Liquid Supply Systems
 Impact of Contaminated Media on 2-Way Solenoid Valve Cores
Impact of Contaminated Media on 2-Way Solenoid Valve Cores
 2 Way Solenoid Valve Performance Differences in Gas and Liquid Media
2 Way Solenoid Valve Performance Differences in Gas and Liquid Media
You May Interest In

Jul 28, 2025 Blog
How to check air solenoid valve?
Jan 14, 2025 Blog
Attention to the Installation of Solenoid Valves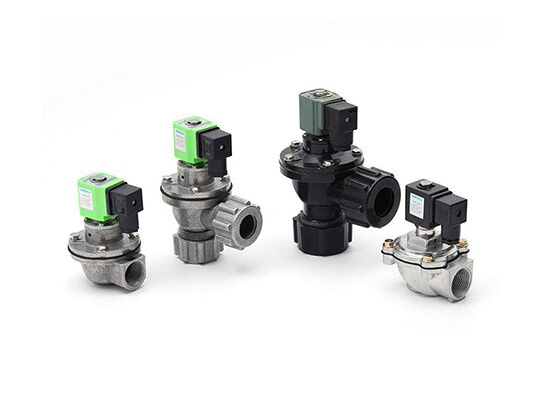


Jul 24, 2025 Blog
How to check the solenoid valve?
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap