Apr 29, 2025
In today's modern industry, certain sectors are placing increasing emphasis on the rapid response of systems. Consequently, the response speed of the media used in these systems is also being enhanced and strengthened as needed. The axial flow channel design of axial valves has gradually gained attention. Their linear-moving valve core design minimizes fluid resistance to the greatest extent, enabling axial valves to perform exceptionally well even under low-pressure, high-flow conditions. Additionally, axial valves can be used in conjunction with external actuator drives, further amplifying their application advantages.
A pneumatic axial flow valve, also known as an axial control valve or axial flow control valve, is a type of flow control valve designed to regulate the flow of compressed air or other media along the axial direction.
The valve core of a linear motion valve moves along the axial direction, minimizing the flow resistance of the fluid medium to the greatest extent. Driven by a pneumatic actuator, its response time is significantly reduced, enabling extremely fast opening and closing operations. This makes it particularly suitable for high-speed, high-pressure systems and space-constrained installations. As mentioned above, these characteristics further enhance its application advantages.
Introduce
The working principle of Pneumatic Axial Valve can be simply summarized as using cylinder compressed air as the power source. Generate linear thrust on the piston of the cylinder, and then the piston rod outside the cylinder directly pushes or pulls the spool of the linear flow control valve. The axial valve core moves axially to open or close the fluid channel. Due to being in the direction of fluid flow, it is highly suitable for high-pressure, high-speed media and compact assembly environments.
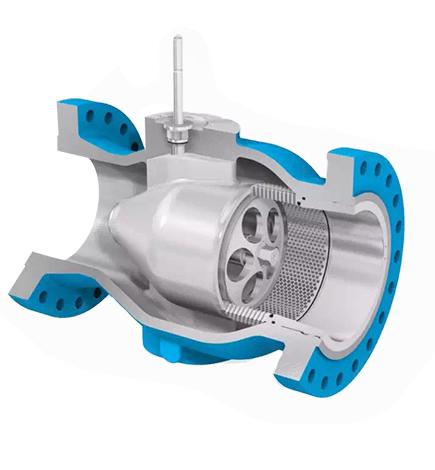

Structure
By understanding the structure and function of each component that makes up the automatically axial valve, one can have a deeper understanding of the entire workflow of the flow control valve. Mainly by utilizing the thrust of the piston rod, the valve core is pushed to move in the direction of the fluid, achieving the function of controlling the fluid.
Valve body: The component where the fluid channel is located, usually a straight through structure.
Valve core: the core component that controls the passage of fluid and moves in a linear motion.
Sealing component: Ensure no leakage when closed.
Pneumatic actuator: converts compressed air energy into linear mechanical action.
Piston rod: connects the actuator and valve core to transmit thrust.
Spring: used for resetting, commonly used in single acting structures.
Guide sleeve and packing box: ensuring the smoothness and sealing of the piston rod's linear motion.

Working Process Detail
The specific workflow of Axial Valve includes two processes: opening and closing. The movement and retraction of the valve core rely on the piston movement of the cylinder:
Initial state:
The pneumatic cylinder has not yet been filled with air.
If it is a single acting structure cylinder, the internal spring keeps the valve in a default state.
Open process:
Supply air to the actuator cylinder:
Control the system to turn on the air source. Compressed air enters one side of the actuator chamber.
Piston motion:
The air pressure pushes the piston to move inside the cylinder, and the piston drives the piston rod outside the cylinder to move forward, transmitting the force to the connected valve core.
Valve core opening:
The valve core, pushed by the piston rod, moves axially along the direction of fluid flow and leaves the valve seat. At this point, the valve opens and the fluid can flow smoothly along the channel.
Closing process:
Gas source switching or exhaust:
In a double acting cylinder, it is necessary to switch the direction of control air pressure or directly disconnect the air source
Reset action:
In the double acting cylinder structure, reverse air pressure pushes the piston back to its original position; In a single acting cylinder structure, the spring force automatically returns the piston and drives the valve core back to the closed position.
Reset the valve core to the valve seat and seal it off:
The valve core presses the valve seat tightly, completely cutting off the fluid channel.
Axial Valve has the following significant characteristics compared to other general valve types:
Direct flow channel: Fluid flows in a straight line along the axial direction, reducing pressure loss.
Quick response: Compared with ordinary pneumatic globe valves, Axial Valve is pneumatically driven, with fast opening and closing speed, suitable for frequent operating conditions.
High sealing performance: Using high-quality sealing components to ensure no leakage when closed.
Compact structure: Axial Valve has a simple overall design, takes up less space, and is easy to install.
Low flow resistance: Due to its straight through design, the Pneumatic Axial Valve has less resistance to the internal flow medium compared to ordinary pneumatic ball valves, making it very suitable for high-frequency switch applications.
Pneumatic Axial Valve, with its unique design and features, can be applied to the following industries:
Oil and gas: Used for pipelines that require rapid opening and closing control.
Chemical industry: Control the flow of corrosive or high viscosity media.
Electric power industry: used for flow regulation of media such as steam and water.
Food and medicine: Control liquid flow in environments with high hygiene requirements.
Automated production line: achieving automatic control and management of fluid systems.
Axial valves are becoming core components in modern industrial fluid control systems due to their advantages of high efficiency, reliability, energy savings, and automation compatibility. They demonstrate particularly outstanding performance in high-pressure, large-flow, and automated scenarios where their superior characteristics can be fully leveraged.
If you want to know more about pneumatic axial valve,or other types of valves.You can browse our products or browse our website:www.fokcavalve.com.Of course you directly contact with us.
 Medium Trapping in Pneumatic Ball Valve Rotation
Medium Trapping in Pneumatic Ball Valve Rotation
 Influence of Insufficient Pneumatic Actuator Torque on Ball Valve Operation
Influence of Insufficient Pneumatic Actuator Torque on Ball Valve Operation
 Cavity Pressure Accumulation: Causes of Abnormal Internal Pressure in Pneumatic Ball Valve
Cavity Pressure Accumulation: Causes of Abnormal Internal Pressure in Pneumatic Ball Valve
 Considerations When Using 3 Way Solenoid Valve in Vacuum Systems
Considerations When Using 3 Way Solenoid Valve in Vacuum Systems
 Switching Efficiency of 3 Way Solenoid Valve in Compressed Air Systems
Switching Efficiency of 3 Way Solenoid Valve in Compressed Air Systems
You May Interest In


Jul 30, 2025 Blog
AWG:Why do We Need the American Wire Gauge?
Jul 28, 2025 Blog
How to check air solenoid valve?
Jul 24, 2025 Blog
How to check the solenoid valve?

Apr 22, 2025 Blog
Pneumatic Globe Control Valve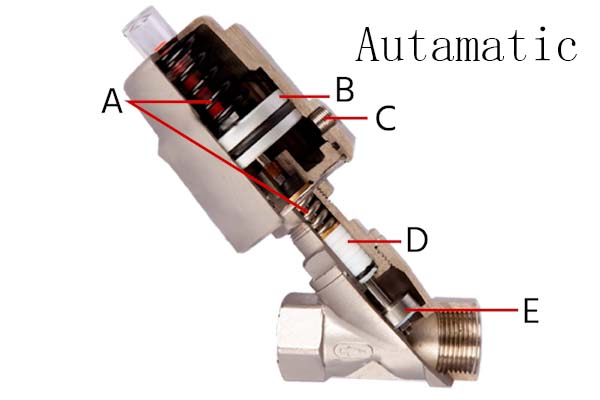
Apr 16, 2025 Blog
A Guide to Understand Angle Seat Valve
Apr 10, 2025 Blog
Limit Switches in Valve Control SystemsFOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap