Nov 21, 2025
The valve seat angle is one of the most critical geometric parameters in valve design, machining, and maintenance. It directly influences airflow, sealing performance, heat transfer, and overall valve efficiency. Whether you’re working with engine valves, general pneumatic valves, or industrial flow-control components such as a pneumatic angle seat valve, pneumatic control angle seat valve, or a pneumatic angle seat flange valve, understanding how to measure and determine the valve seat angle is essential. For manufacturers and suppliers, accurate valve seat angle evaluation is key to ensuring product reliability and performance.
In the following sections, we’ll explain why the valve seat angle is so important, what angles are commonly used in different applications, and how to measure the valve seat angle correctly and verify the accuracy of your results. This article is designed to give you a clearer, more practical understanding of valve seat angle measurement.
A correct valve seat angle is essential for achieving reliable performance in any valve system. With the proper angle, the valve can seal tightly, preventing leakage and ensuring consistent pressure. It also supports smoother airflow or fluid flow.In addition, an accurate angle reduces heat concentration and uneven wear, helping extend the overall lifespan of the valve. Most importantly, a well-designed seat angle improves overall system efficiency—particularly in engines, where it plays a major role in maintaining stable combustion and performance.
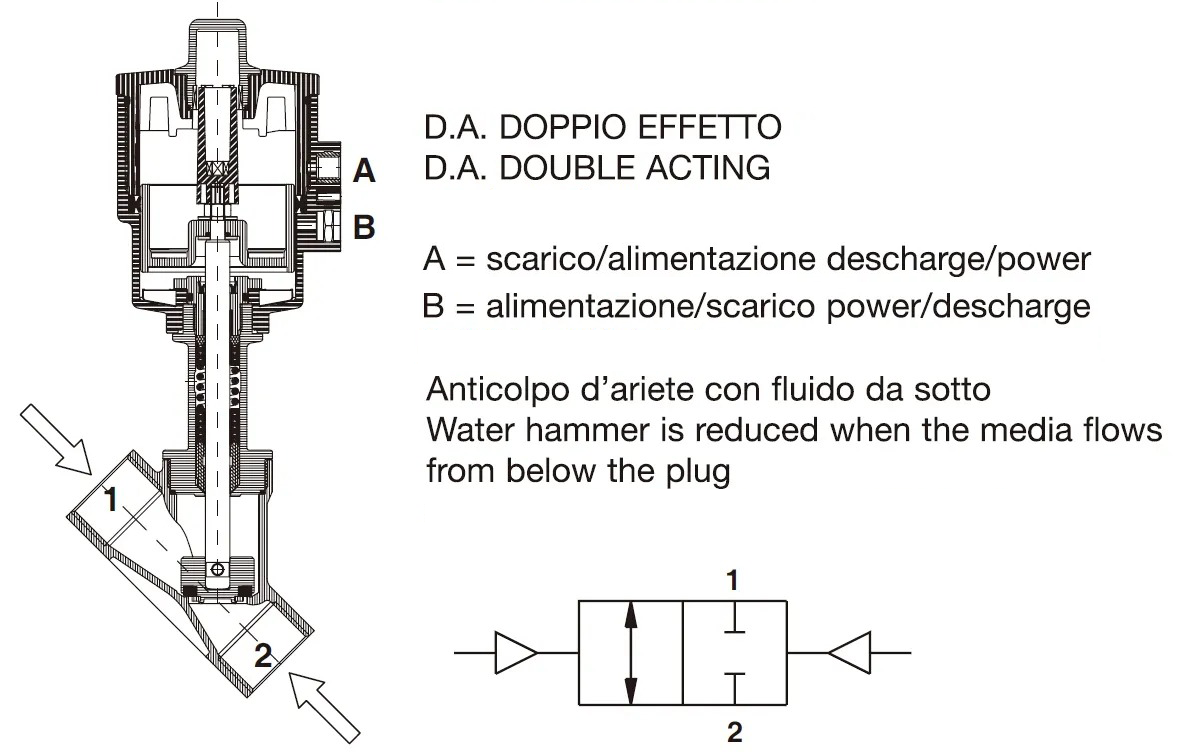
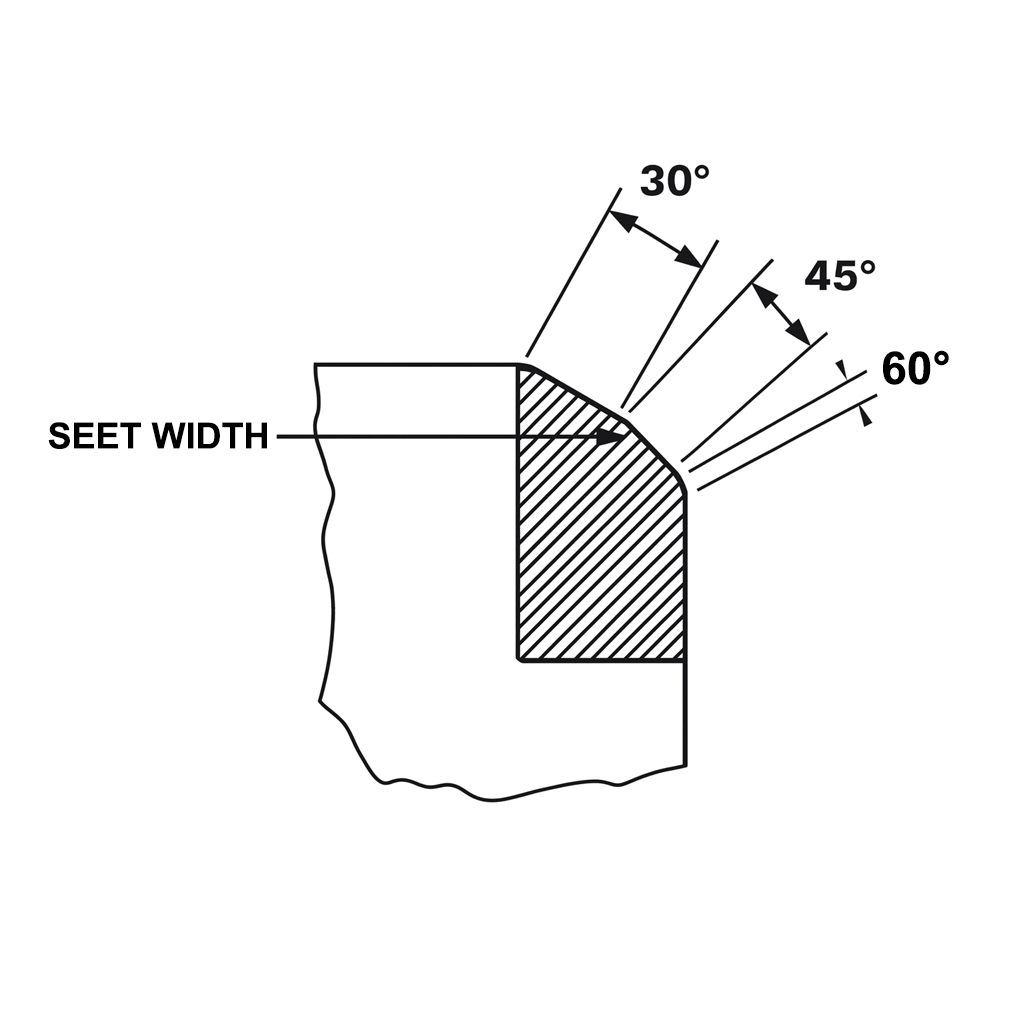
Common valve seat angles include:
30°45°60°75° Among these, 45° is the most widely used in many engine and pneumatic valve designs, offering a balance between flow and sealing strength.
Because a valve does not suddenly open, remain fully open for a period, and then suddenly close. Instead, it accelerates upward off its seat and reaches its maximum lift velocity at about 25% of its total lift. After that, the valve must begin to slow down so it can reverse direction at full lift and then accelerate downward again toward closure. Since the valve stays at full lift for only a very brief moment, most of its open duration is actually spent at partial lift.
This means that the small gap between the valve and its 45-degree seat which is the smallest flow cross-section in the entire intake passage becomes the area with the highest flow velocity.
Below are the most common and reliable methods to determine a valve seat angle.
Use a Valve Seat Gauge or Valve Seat Angle Tool
Measure Using a Protractor or Digital Angle Finder
Check Manufacturer Specifications
Optical Measurement (Profile Projector)
Dye and Lapping Contact Pattern Method
Best for: Workshops, engine rebuilders, precision measurement
A dedicated valve seat gauge can measure the angle with high accuracy.
Steps:
1.Clean the valve and seat area.
2.Position the gauge on the valve face.
3.Rotate or lock the tool until the angle indicator aligns.
4.Read the displayed angle (usually in degrees).
Pros: Very accurate
Cons: Requires specialized tools
Best for: General maintenance, quick checks
Steps:
1.Place the valve in a vise or stable fixture.
2.Align the protractor base along the valve stem.
3.Match the angle finder edge with the valve face.
4.Read the angle displayed.
This method provides a good estimate but may not be suitable for high-precision applications.
Pro Tip: Digital angle finders provide better accuracy than manual protractors.
Best for: OEM valves, standardized components
If you're working with: Automotive engines/Pneumatic angle seat valves/Industrial process valves
…the valve seat angle is usually stated in the technical manual or parts catalog.
Benefits: 100% accurate.No measurement errors
Best for: Precision machining, QA inspections
A profile projector or optical comparator projects the valve profile onto a screen for precise measurement.
Steps:
1.Place the valve on the measuring fixture.
2.Focus the profile image.
3.Align the seat angle against the screen grid.
4.Read the angle precisely.
Accuracy: Very high
Common in: Machine shops, QC departments
Best for: Confirming angle match between seat and valve
This is not a direct angle measurement, but it helps verify if the valve face and seat angles match properly.
Steps:
1.Apply layout dye or lapping compound to the seat.
2.Lightly rotate the valve on the seat.
3.Observe the contact patch.
If contact is even, the angles match. If not, the angles differ.
If the angle is incorrect, it can lead to issues such as leakage or pressure loss, poor engine compression (in internal combustion engines), uneven or narrow contact surfaces, excessive wear on one side, abnormal noise or vibration, reduced flow efficiency, and other similar problems.
| Category | Typical Angle | Notes |
| Engine Valves | Intake: ~30°Exhaust: ~45° | Standard angles used in internal combustion engines |
| Industrial & Pneumatic Valves | ~45°–75° | Angle seat valves often use optimized flow-seat geometry |
| High-Pressure / Steam Valves | 60° or higher | Sharper angles improve sealing under high temperature and pressure |
1. What is the most common valve seat angle?
45° is the most common across many valve applications.
2. What happens if the valve seat angle is wrong?
The valve will not seal correctly, causing leakage, pressure loss, or overheating.
3. Can I measure valve seat angle without special tools?
Yes. A protractor or digital angle finder can provide a rough measurement.
4. Do angle seat valves always use the same seat angle?
No. Industrial angle seat valves vary depending on design and flow requirements.
Determining the valve seat angle is essential for proper sealing, flow performance, and long-term stability of any valve system. By using the right tools—whether a simple protractor or high-precision optical equipment—you can measure and verify valve seat angles accurately. Contact us for more product information: Fokcavalve.com
(FK9026)
 Fluid Retention During Supply and Exhaust Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
Fluid Retention During Supply and Exhaust Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
 Pressure Fluctuation During Flow Path Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
Pressure Fluctuation During Flow Path Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
 Control Characteristics of 2-Way Solenoid Valves in Intermittent Liquid Supply Systems
Control Characteristics of 2-Way Solenoid Valves in Intermittent Liquid Supply Systems
 Impact of Contaminated Media on 2-Way Solenoid Valve Cores
Impact of Contaminated Media on 2-Way Solenoid Valve Cores
 2 Way Solenoid Valve Performance Differences in Gas and Liquid Media
2 Way Solenoid Valve Performance Differences in Gas and Liquid Media
You May Interest In


Jul 30, 2025 Blog
AWG:Why do We Need the American Wire Gauge?
Jul 28, 2025 Blog
How to check air solenoid valve?
Jul 24, 2025 Blog
How to check the solenoid valve?

Apr 22, 2025 Blog
Pneumatic Globe Control Valve
Apr 16, 2025 Blog
A Guide to Understand Angle Seat Valve
Apr 10, 2025 Blog
Limit Switches in Valve Control SystemsFOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap