Feb 06, 2026
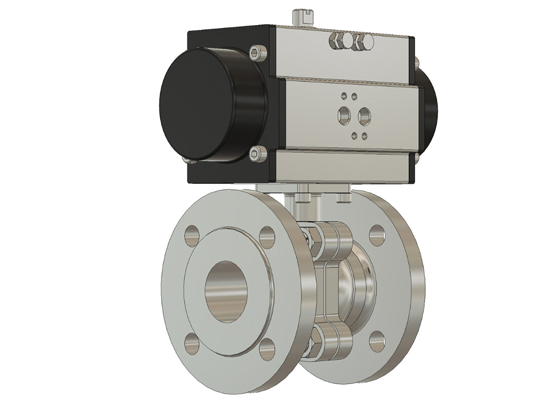
The reliability of a pneumatic ball valve largely depends on whether the actuator can deliver adequate torque. Many systems perform well during commissioning yet fail in real production, where the valve cannot fully open or close. The root cause is often an undersized pneumatic ball valve actuator rather than a defect of the valve body itself. Understanding this issue requires a clear view of the real resistance during valve movement.
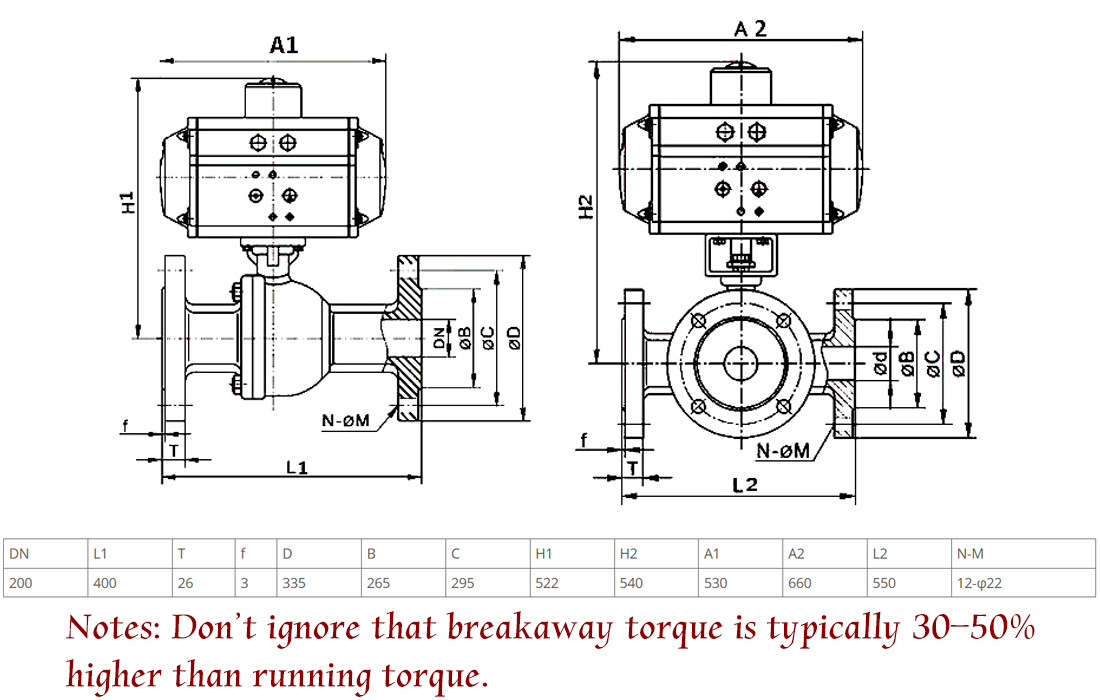
Ball valve operation is not a simple rotation. Seat preload, medium pressure acting on the ball, and friction coefficient of sealing surfaces all convert into actuator load. In high pressure pneumatic ball valve applications or media containing particles, friction can be far higher than theoretical values. When engineers rely only on a pneumatic ball valve sizing chart, they may ignore that breakaway torque is typically 30–50% higher than running torque.
For stainless steel pneumatic ball valve 316 used in steam or chemical service, harder seats and thermal expansion further increase the demand. Applying water-system experience to these conditions often leads to hidden risk.
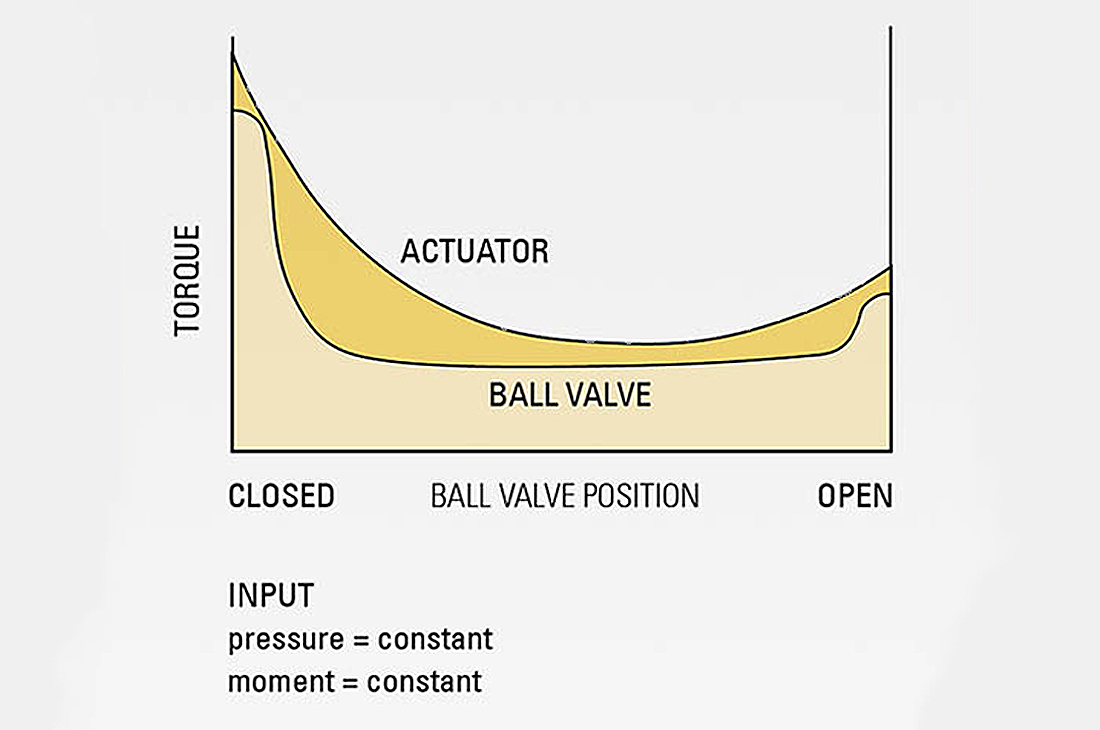
The most common symptom is a half-open position. The ball fails to reach the 90-degree end point, causing unstable flow and misleading process alarms. In automated lines, this is frequently mistaken as a control logic issue instead of a limitation of pneumatic ball valve automation.
Sticking is another problem. Compact pneumatic ball valve installed in tight spaces may suffer uneven stem load. With a single acting pneumatic ball valve, the return torque is smaller, so failures occur more often than with a double acting pneumatic ball valve.
| Application condition | Influence on torque |
|---|---|
| Steam or high temperature | Seat expansion increases friction |
| Gas with impurities | Particle embedding raises breakaway torque |
| Chemical process | Corrosion changes surface roughness |
| Low temperature | Lubrication performance decreases |
Experience shows that the torque of pneumatic ball valve for steam can be over 40% higher than that of pneumatic ball valve for gas. In pneumatic ball valve for oil & gas, long-term deposits add extra resistance.
Insufficient torque affects the whole pneumatic ball valve control system. Operating at the limit accelerates wear of seals and gears, reducing positioning accuracy. When users compare pneumatic ball valve vs electric ball valve, the sensitivity of pneumatic torque reserve is often overlooked.
For a spring return pneumatic ball valve, inadequate closing torque may prevent safe reset during air loss, creating serious safety concerns.
The safe method is to multiply calculated torque by a service factor and correct it according to real media and temperature. For critical positions, choose adjustable pneumatic ball valve with actuator or follow a professional pneumatic ball valve installation guide to ensure sufficient air supply.
In integrated layouts, pressure drop in pneumatic ball valve manifold mounting can also reduce actual output. Only by evaluating valve, actuator, and working condition as a whole can a quarter turn pneumatic ball valve deliver long-term reliability in automation systems.
(FK9025)
 Medium Trapping in Pneumatic Ball Valve Rotation
Medium Trapping in Pneumatic Ball Valve Rotation
 Influence of Insufficient Pneumatic Actuator Torque on Ball Valve Operation
Influence of Insufficient Pneumatic Actuator Torque on Ball Valve Operation
 Cavity Pressure Accumulation: Causes of Abnormal Internal Pressure in Pneumatic Ball Valve
Cavity Pressure Accumulation: Causes of Abnormal Internal Pressure in Pneumatic Ball Valve
 Considerations When Using 3 Way Solenoid Valve in Vacuum Systems
Considerations When Using 3 Way Solenoid Valve in Vacuum Systems
 Switching Efficiency of 3 Way Solenoid Valve in Compressed Air Systems
Switching Efficiency of 3 Way Solenoid Valve in Compressed Air Systems
You May Interest In


Jan 08, 2026 Blog
Why Globe Valves Cannot Fully Replace Ball Valves


FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap