Feb 04, 2026

In compressed air automation, the 3 way solenoid valve is responsible for converting supply and exhaust paths within milliseconds. Because air is compressible, pressure does not rise or fall instantly. The dynamic behavior of gas makes the switching speed of a 3/2 way solenoid valve highly dependent on valve structure, pipe volume, and exhaust conditions.
When the coil of a 3-way pneumatic solenoid valve is energized, the spool shifts and the air stored in the circuit must redistribute to the actuator chamber. If the flow area is small or the exhaust path is long, the elastic nature of air slows the pressure transition. Engineers often notice that identical 3 way solenoid valves behave differently on separate machines, which is mainly caused by variations in system volume and back pressure.
The advantage of a three-port design is that one body completes both supply and release. Compared with two-port solutions, the exhaust port valve 3 way shortens the pneumatic path and improves the return speed of single-acting cylinders. However, when silencers or fittings restrict the outlet, the release process becomes the limiting factor of 3 way solenoid valve switching.
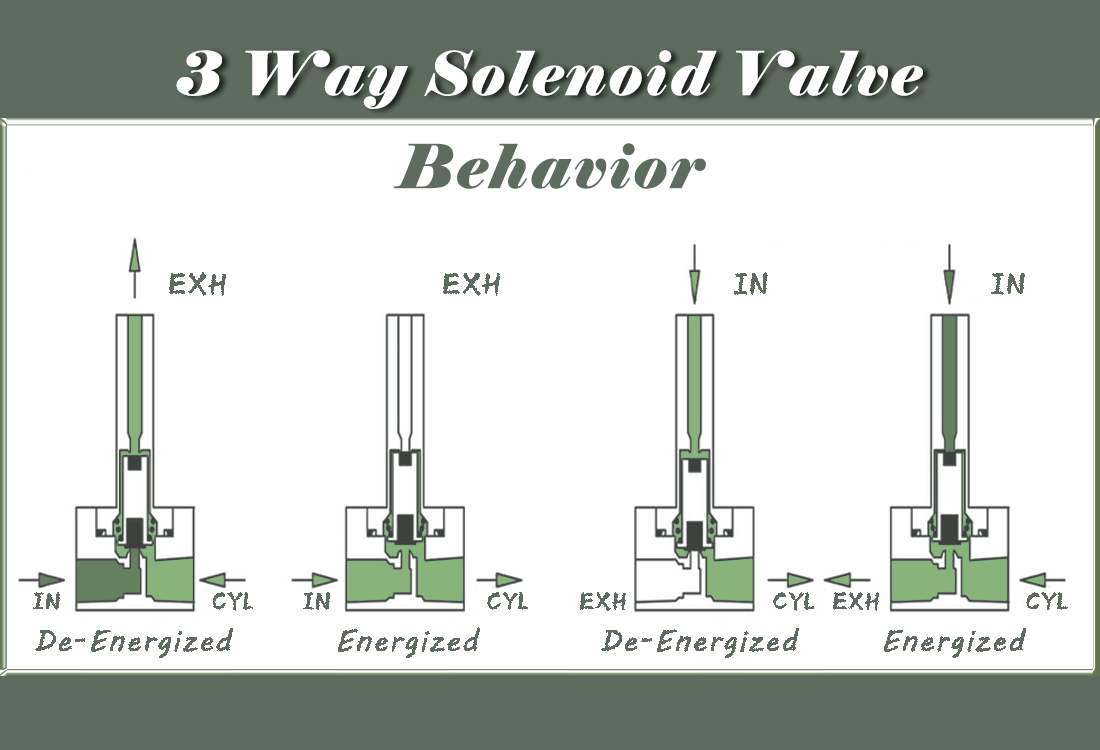
The driving force of the spool comes from magnetic power or pilot pressure. A 3 way direct acting solenoid valve relies on electromagnetic force to overcome spring and media pressure, suitable for small or medium flow. A 3 way pilot operated solenoid valve uses a small control flow to move a larger main spool and normally achieves higher efficiency under stable supply pressure.
System layout also plays a decisive role. Long hoses increase effective volume and delay the build-up of pressure at the actuator. Using 3 way solenoid valve manifold mounting reduces dead volume and is widely adopted in industrial automation solenoid valves to gain faster cycles.
| Item | Effect on Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Hose length | Longer → slower response |
| Exhaust resistance | Higher → delayed release |
| Valve type | Pilot type faster with stable air |
| Coil voltage | Low voltage weakens motion |
Selection should not rely only on nominal Cv. For packaging machines or pick-and-place units, the smoothness of the exhaust path is more critical than peak inlet flow. A compact 3 way solenoid valve with optimized port geometry often performs better than a larger valve installed with restrictive fittings. The real efficiency of a 3 way valve for pneumatic cylinder is determined by the entire circuit.
Some users expect a high speed 3 way solenoid valve to solve all delays, but if back pressure remains high, the improvement will be limited. Reducing bends, choosing low-resistance silencers, and keeping the valve close to the actuator are more effective methods.
Poor switching efficiency also affects durability. When exhaust is obstructed, the spool of a solenoid valve 3 way control works under unbalanced pressure, accelerating seal wear. Stable release conditions help maintain consistent cycle life of the AC/DC 3 way solenoid valve and reduce air consumption.
Understanding how compressed air behaves inside the valve explains why some systems react sharply while others feel sluggish. With correct layout and a suitable fast response 3 way solenoid valve, the pneumatic system can achieve both speed and long-term reliability.
(FK9025)
 Medium Trapping in Pneumatic Ball Valve Rotation
Medium Trapping in Pneumatic Ball Valve Rotation
 Influence of Insufficient Pneumatic Actuator Torque on Ball Valve Operation
Influence of Insufficient Pneumatic Actuator Torque on Ball Valve Operation
 Cavity Pressure Accumulation: Causes of Abnormal Internal Pressure in Pneumatic Ball Valve
Cavity Pressure Accumulation: Causes of Abnormal Internal Pressure in Pneumatic Ball Valve
 Considerations When Using 3 Way Solenoid Valve in Vacuum Systems
Considerations When Using 3 Way Solenoid Valve in Vacuum Systems
 Switching Efficiency of 3 Way Solenoid Valve in Compressed Air Systems
Switching Efficiency of 3 Way Solenoid Valve in Compressed Air Systems
You May Interest In
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap