Dec 31, 2025
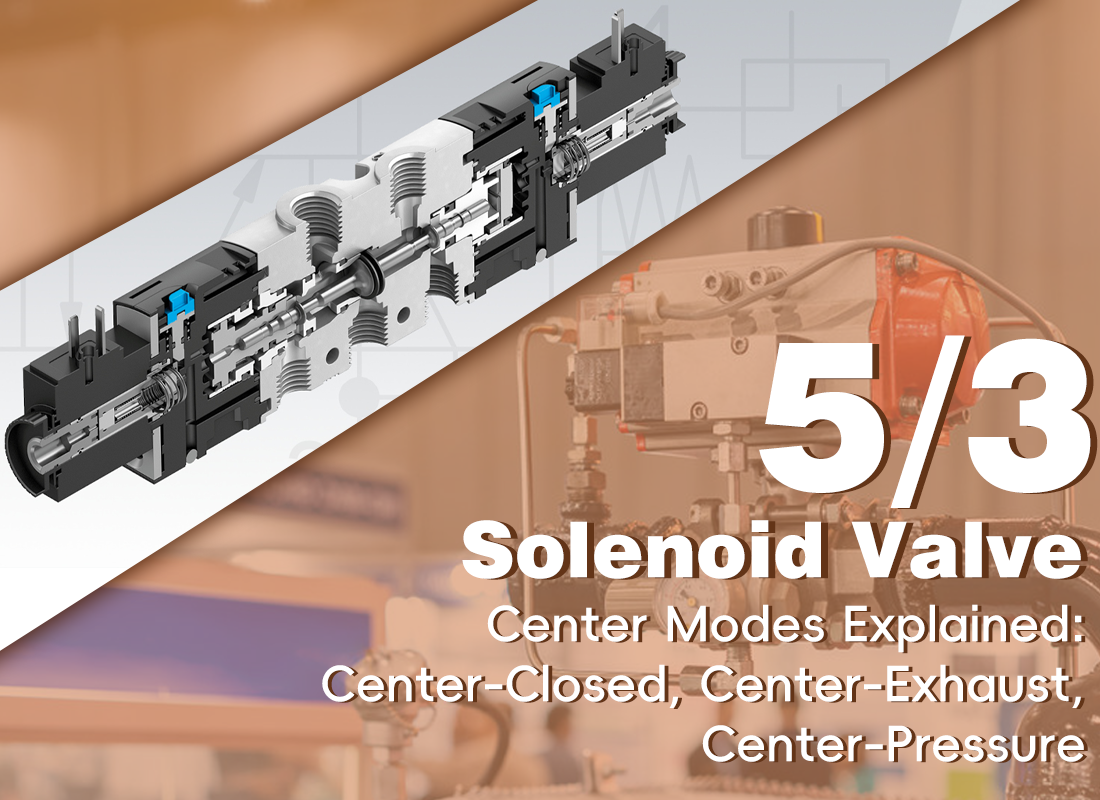
In pneumatic control systems, 5/3 solenoid valves are widely recognized as essential components in industrial automation, thanks to their versatile operating positions that enable precise control over downstream equipment. Unlike 2-way solenoid valves that only have two states (on and off), 5/3 solenoid valves feature an additional central position where the valve spool can stay when the power or signal is cut off. This unique design greatly enhances the flexibility of valve operation and allows for more sophisticated control of pneumatic actuators.
The three common center positions—center-closed, center-exhaust, and center-pressure—are the core of this flexibility, as they determine the valve’s behavior when de-energized, directly impacting the movement of pneumatic cylinders and other actuators, as well as the overall pneumatic system safety.
The key characteristics, functions and typical applications of the three modes are summarized in the table below:
| Mode Type | Valve Spool Position Feature | Core Function | Typical Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| Center-Closed | All five ports fully sealed; no air inlet or outlet | Actuator locking; maintain current position | Precision machining fixture positioning; workpiece clamping in automated production lines |
| Center-Exhaust | Supply port blocked; output ports connected to exhaust ports | Rapid pressure relief; actuator reset | Emergency stop in assembly lines; stamping equipment safety protection |
| Center-Pressure | Exhaust ports blocked; supply port delivers air to both output ports | Continuous pressure supply; load balancing | Double-acting cylinder clamping force maintenance; heavy-duty material handling equipment |
Center-closed is a mode where all five ports of the 5/3 solenoid valve are completely sealed when the valve spool position is in the center. In this state, the supply port is blocked from delivering compressed air, and the connection between the output ports and exhaust ports is fully cut off, preventing any air flow in or out of the system. For downstream devices, this means the compressed air inside the pneumatic actuator is trapped, and the actuator can maintain its current position without any displacement caused by air leakage or pressure loss.
This actuator locking capability makes center-closed valves ideal for applications that require long-term position retention. For example, in the material positioning process of automated production lines, after a hydraulic clamp holds a workpiece, a short power outage or signal interruption will not affect the clamp’s position if a center-closed valve is used, effectively avoiding workpiece deviation or falling. In the fixture system of precision machining, the position-locking function of center-closed valves ensures that machining accuracy is not compromised by unexpected actuator movements. By preventing misoperation of downstream equipment in emergency situations, center-closed valves play a critical role in improving production safety.
In center-exhaust mode, the supply port of the 5/3 solenoid valve is blocked when the valve spool is in the center position, while both output ports are connected to the exhaust ports. This connection allows the compressed air inside the pneumatic actuator to be quickly released through the exhaust ports, leading to a rapid drop in system pressure. Without air pressure support, the actuator will return to its initial position under the action of its own weight or spring force, or remain in an unpowered state.
Known as a rapid reset valve, the center-exhaust valve excels in scenarios that require quick actuator reset or emergency pressure relief. In automated assembly lines, if a defective workpiece is detected or an emergency stop signal is triggered, the center-exhaust valve can immediately empty the air in the cylinder, allowing the mechanical gripper to release the workpiece quickly and avoid deformation caused by prolonged clamping. In the safety protection system of stamping equipment, the center-exhaust valve can rapidly release actuator pressure once an abnormal signal is received, preventing collisions between machine components. This makes center-exhaust valves a key configuration for ensuring the safe operation of industrial equipment.
Center-pressure mode is characterized by the blocking of both exhaust ports when the valve spool is in the center position, while the supply port delivers compressed air to both output ports simultaneously. This design ensures that even when there is no electrical signal input to the valve, the pneumatic actuator can still receive a stable supply of compressed air, enabling it to maintain its preset position or achieve load balancing.
As a load balancing valve, center-pressure valves are widely used in mechanical systems that require continuous torque maintenance or load balancing, especially in the control of double-acting cylinders. For instance, in heavy-duty material handling equipment, after a double-acting cylinder clamps a heavy object, a power outage will not cause the object to slip because the center-pressure valve continues to supply air to the cylinder, maintaining the clamping force.
In the tension control link of automated production lines, center-pressure valves can keep the actuator outputting stable pressure, ensuring balanced tension during material transmission. With the ability to maintain pressure without electrical signals, center-pressure valves balance actuator control accuracy and system safety, making them a common choice in complex pneumatic circuit design.
When designing a pneumatic control system, the selection of the 5/3 solenoid valve’s center mode should be based on comprehensive considerations of actuator type, operational requirements, and system safety standards:
◆ Center-closed valves are preferred for scenarios that require position locking and long-term actuator position retention, such as fixture positioning in precision machining and workpiece fixing in assembly lines.
◆ Center-exhaust valves are suitable for applications that need rapid reset, emergency pressure relief, or actuator return in case of system failure, such as gripper control in automated assembly lines and safety protection in stamping equipment.
◆ Center-pressure valves are ideal for systems that require continuous torque maintenance or load balancing, such as clamping control of double-acting cylinders and load stabilization in material handling equipment.
Proper selection of the center mode for 5/3 solenoid valves not only optimizes the operational logic of actuators but also significantly improves the reliability and flexibility of the entire pneumatic system, providing a solid guarantee for the efficient operation of industrial automation production.
(FK9025)
 Influence of Air Reservoir Volume on Pulse Solenoid Valve Blowing Performance
Influence of Air Reservoir Volume on Pulse Solenoid Valve Blowing Performance
 How Diaphragm Material Affects Pulse Solenoid Valve Response Speed
How Diaphragm Material Affects Pulse Solenoid Valve Response Speed
 Effect of Diaphragm Aging on Pulse Solenoid Valve Blowing Performance
Effect of Diaphragm Aging on Pulse Solenoid Valve Blowing Performance
 Pulse Solenoid Valve Back-Blowing Interval and System Pressure Drop
Pulse Solenoid Valve Back-Blowing Interval and System Pressure Drop
 Instant High Flow Release: How Pulse Solenoid Valve Generates Strong Jet Intensity
Instant High Flow Release: How Pulse Solenoid Valve Generates Strong Jet Intensity
You May Interest In





Dec 31, 2025 Blog
Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Manual Button Explained

FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap