Dec 26, 2025

In industrial automation and fluid control systems, solenoid valves are among the most widely used actuators. Their performance and lifespan are closely related to the type of coil—DC (direct current) or AC (alternating current). Choosing the right solenoid valve coil affects not only the stability and safety of the valve but also noise levels and operational efficiency. This article provides a detailed comparison of DC and AC coils to help engineers make informed decisions.
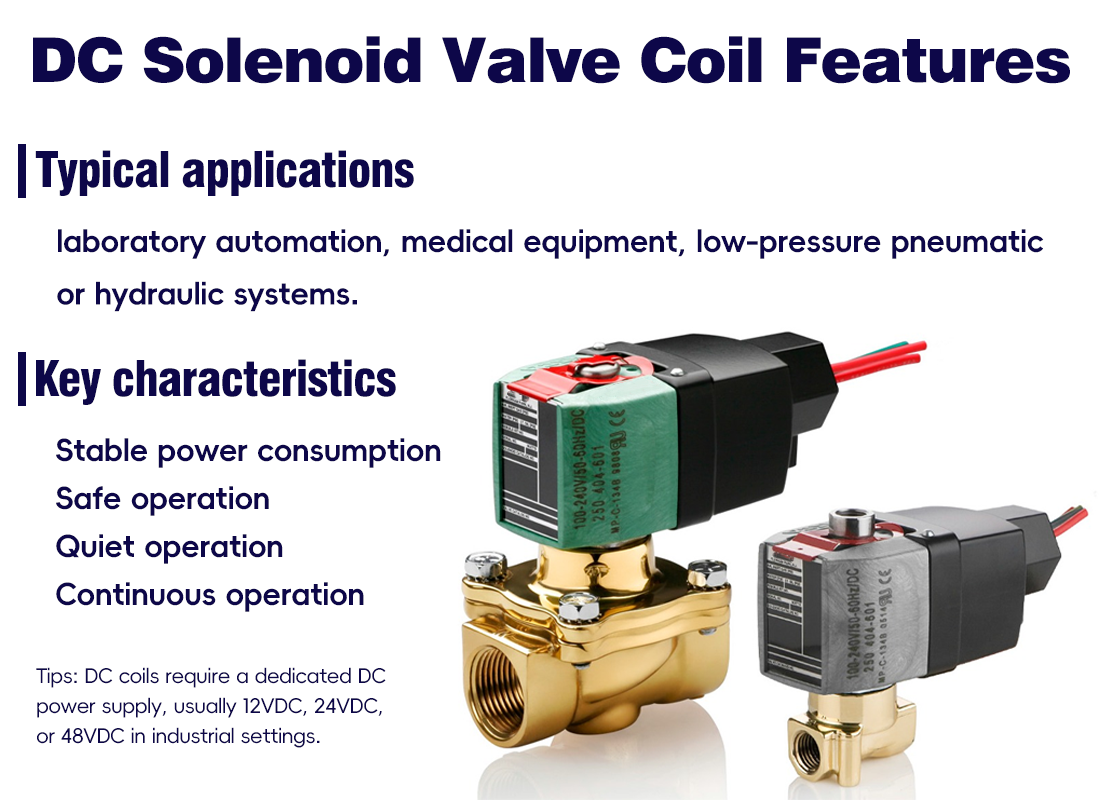
DC (Direct Current) coils are commonly used in low-voltage or precision control systems. Key characteristics include:
◆ Stable power consumption: DC current remains constant, ensuring consistent coil power and reducing fluctuations.
◆ Safe operation: Lower voltage levels reduce the risk of electrical hazards, even during long-term operation.
◆ Quiet operation: Unlike AC coils, DC coils do not generate a fluctuating magnetic field, resulting in virtually no noise—ideal for noise-sensitive environments.
◆ Continuous operation: DC coils can remain energized for long periods without overheating, making them suitable for extended run applications.
◆ Typical applications: laboratory automation, medical equipment, low-pressure pneumatic or hydraulic systems. DC coils require a dedicated DC power supply, usually 12VDC, 24VDC, or 48VDC in industrial settings.
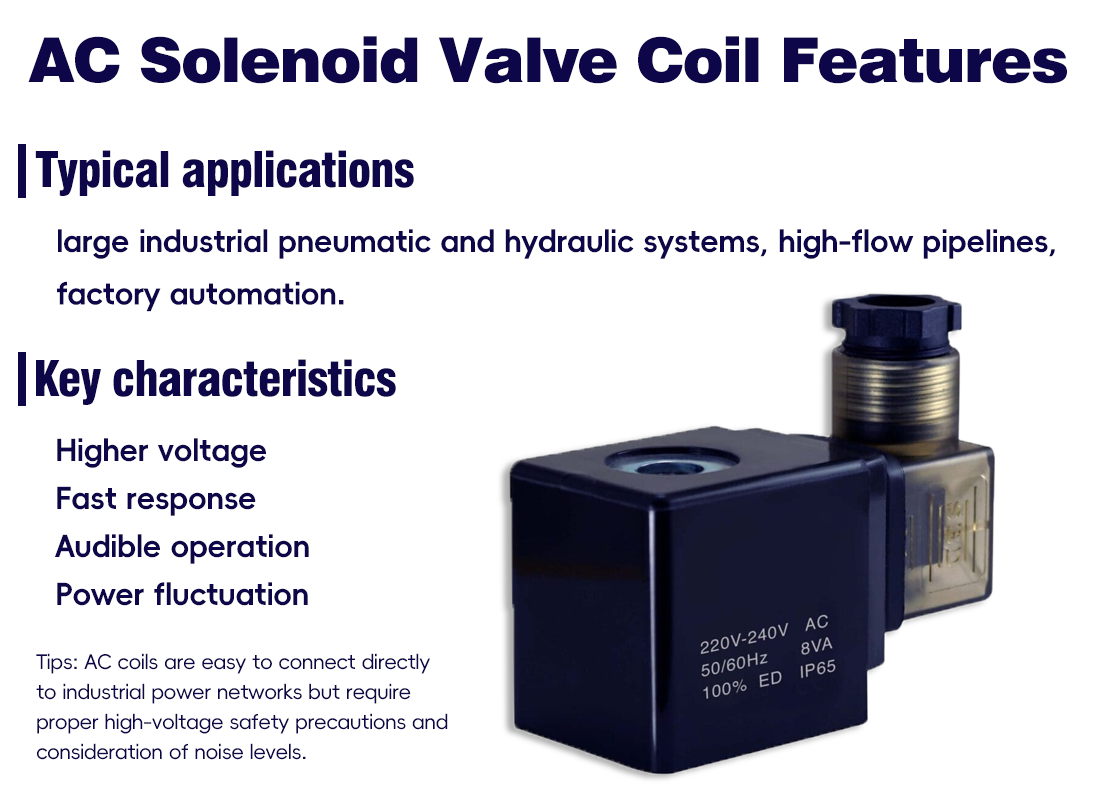
AC (Alternating Current) coils are widely used in industrial electrical systems, especially in high-voltage or high-flow applications. Key characteristics include:
◆ Higher voltage: AC coils commonly operate at 110V or 220V, suitable for large solenoid valves.
◆ Fast response: The alternating magnetic field creates higher actuation force, resulting in quicker valve opening and closing.
◆ Audible operation: AC coils naturally produce a slight humming sound during operation due to the alternating magnetic field.
◆ Power fluctuation: AC current varies with time, which may slightly affect valve stability in high-precision applications.
◆ Typical applications: large industrial pneumatic and hydraulic systems, high-flow pipelines, factory automation. AC coils are easy to connect directly to industrial power networks but require proper high-voltage safety precautions and consideration of noise levels.
| Feature | DC Coil | AC Coil |
|---|---|---|
| Power Type | Direct Current | Alternating Current |
| Power Stability | High, constant | Varies with AC waveform |
| Noise | Quiet | Slight humming |
| Response Speed | Slower | Fast |
| Safety | Lower voltage, safer | Higher voltage, requires precautions |
| Typical Use | Precision control, long continuous operation | High flow, industrial network applications |
From this comparison, DC coils are ideal when stability, safety, and low noise are priorities, while AC coils are preferable for rapid response and high-power output.
① Check the power supply: The system’s available voltage (DC or AC) determines the coil type.
② Consider the environment: DC coils are better in noise-sensitive settings, while AC coils suit high-voltage industrial pipelines.
③ Valve response requirements: For fast actuation, AC is recommended; for long-duration precision control, DC is preferable.
④ Safety and maintenance: DC coils are inherently safer for long-term operation; AC coils require proper grounding and periodic inspection.
⑤ Power and efficiency: DC coils generate less heat and maintain efficiency during long-term energization; AC coils respond quickly but may produce noise and heat under continuous operation.
There is no absolute “better” choice between DC and AC solenoid valve coils. The decision depends on power supply type, application requirements, and operational conditions. DC coils offer safety, low noise, and long-life performance for precision or continuous operations, while AC coils provide high-speed actuation and high-power capability for industrial pipelines and automation networks. Understanding these differences ensures reliable and stable valve control in pneumatic, hydraulic, and fluid systems.
(FK9025)
 How Diaphragm Material Affects Pulse Solenoid Valve Response Speed
How Diaphragm Material Affects Pulse Solenoid Valve Response Speed
 Effect of Diaphragm Aging on Pulse Solenoid Valve Blowing Performance
Effect of Diaphragm Aging on Pulse Solenoid Valve Blowing Performance
 Pulse Solenoid Valve Back-Blowing Interval and System Pressure Drop
Pulse Solenoid Valve Back-Blowing Interval and System Pressure Drop
 Instant High Flow Release: How Pulse Solenoid Valve Generates Strong Jet Intensity
Instant High Flow Release: How Pulse Solenoid Valve Generates Strong Jet Intensity
 Influence of Air Supply Pressure Fluctuation on Pneumatic Axial Valve Operation
Influence of Air Supply Pressure Fluctuation on Pneumatic Axial Valve Operation
You May Interest In



Dec 23, 2025 Blog
How Actuator Size Affects Valve Performance













FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap