Dec 25, 2025

In industrial automation and fluid control systems, solenoid valves are among the most commonly used actuators. However, selecting the right type of solenoid valve is crucial for system reliability and performance. This article compares 2-way solenoid valves with pneumatic solenoid valves (commonly two-position three-way or five-way valves) to help users make informed decisions.

Pneumatic solenoid valves, typically two-position three-way or five-way valves, are primarily used to control the switching of air circuits in pneumatic systems. They usually have aluminum bodies, which are lightweight and cost-effective. Because they control compressed air rather than liquid, flow requirements are generally not strict, and most designs include exhaust ports to quickly release excess air, ensuring fast and smooth actuator movement.
These valves are widely used in automated production lines, pneumatic cylinder control systems, and applications that require frequent air circuit switching. For example, a two-position five-way valve can control the forward and backward motion of a double-acting cylinder, while a two-position three-way valve is commonly used for single-acting cylinders or simple air on/off control.
• Body material: Aluminum
• Controlled medium: Compressed air
• Flow requirement: Moderate, not strict
• Exhaust ports: Usually present
• Typical applications: Pneumatic systems, automation lines, cylinder control
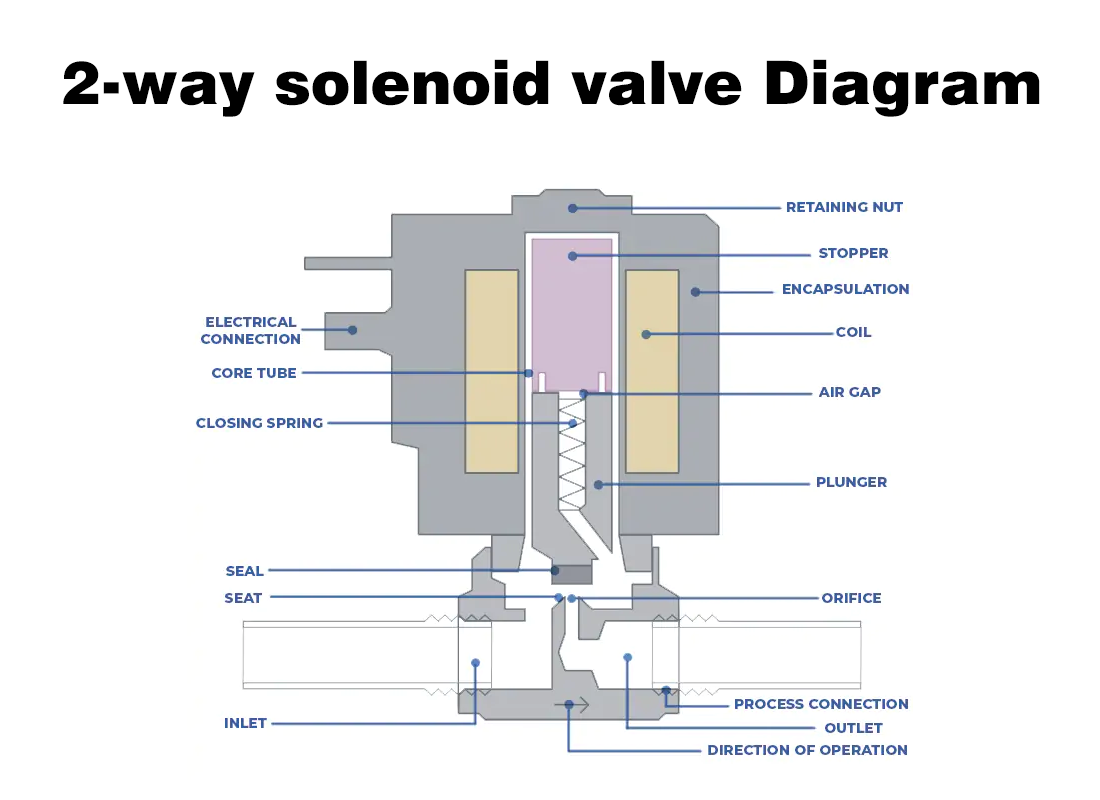
Unlike pneumatic solenoid valves, 2-way solenoid valves are mainly used for on/off control of liquids or gases, such as water, oil, or air. They are usually made of copper or stainless steel, offering durability and corrosion resistance. These valves have strict flow control requirements and usually do not have exhaust ports, because venting could cause leakage or system failure.
2-way solenoid valves are commonly used in fluid control systems, hydraulic circuits, cooling systems, and chemical process flows. For instance, in chemical processing, they can quickly control the flow of solutions; in water treatment systems, they act as main on/off valves; in oil circuits, they ensure precise control of fluid delivery.
• Body material: Copper or stainless steel
• Controlled medium: Air, water, oil, and other fluids
• Flow requirement: Strict, precise control needed
• Exhaust ports: Typically none
• Typical applications: Liquid control systems, oil circuits, chemical processing, water treatment
| Feature | Pneumatic Solenoid Valve (2/3-way or 2/5-way) | 2-Way Solenoid Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Body material | Aluminum | Copper / Stainless Steel |
| Controlled medium | Compressed air | Air, water, oil, other fluids |
| Flow requirement | Moderate | Strict |
| Exhaust port | Usually present | None |
| Primary function | Air circuit switching, cylinder control | Fluid on/off control |
| Typical applications | Automation lines, pneumatic systems | Chemical, hydraulic, oil circuits, water treatment |
Although both are electrically controlled valves, their design purpose, medium compatibility, and flow characteristics differ significantly. Using a pneumatic solenoid valve for liquids may result in leakage or poor performance, while using a 2-way solenoid valve in a pneumatic system may reduce response speed or block airflow.
◆ Identify the controlled medium: Use pneumatic valves for air systems and 2-way solenoid valves for liquid or multi-medium systems.
◆ Check flow and pressure requirements: Liquid or oil systems require precise flow control and appropriate valve sizing.
◆ Consider installation environment and corrosion resistance: For chemical, food, or water systems, choose copper or stainless steel 2-way solenoid valves.
◆ Automation system complexity: Multi-circuit air systems are best served by pneumatic solenoid valves, while single-circuit on/off control favors 2-way solenoid valves.
While 2-way solenoid valves and pneumatic solenoid valves share similar names, their applications and designs are fundamentally different. 2-way solenoid valves are intended for liquids and various media, feature copper or stainless steel bodies, strict flow control, and no exhaust ports. Pneumatic solenoid valves, on the other hand, are used for air circuits, have aluminum bodies, and include exhaust ports. Understanding these differences is essential for reliable operation of automation and fluid systems.
If you need these two types of solenoid valves, you can contact us directly.
(FK9025)
 How Diaphragm Material Affects Pulse Solenoid Valve Response Speed
How Diaphragm Material Affects Pulse Solenoid Valve Response Speed
 Effect of Diaphragm Aging on Pulse Solenoid Valve Blowing Performance
Effect of Diaphragm Aging on Pulse Solenoid Valve Blowing Performance
 Pulse Solenoid Valve Back-Blowing Interval and System Pressure Drop
Pulse Solenoid Valve Back-Blowing Interval and System Pressure Drop
 Instant High Flow Release: How Pulse Solenoid Valve Generates Strong Jet Intensity
Instant High Flow Release: How Pulse Solenoid Valve Generates Strong Jet Intensity
 Influence of Air Supply Pressure Fluctuation on Pneumatic Axial Valve Operation
Influence of Air Supply Pressure Fluctuation on Pneumatic Axial Valve Operation
You May Interest In


Dec 23, 2025 Blog
How Actuator Size Affects Valve Performance










FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap