Jan 13, 2026

In high-temperature steam or hot water systems, solenoid valves are often among the first components to show reliability issues. Engineers frequently report internal leakage or unstable operation after extended exposure to heat. In most cases, the root cause lies not in the coil, but in the sealing system reaching its material limits.
High-temperature media affect every internal component of a solenoid valve, but sealing materials are the most vulnerable. Elastomer seals are designed with defined temperature limits. When operating close to or beyond these limits, their mechanical properties degrade over time.
Steam systems rarely operate at a perfectly stable temperature. Start-up cycles, load fluctuations, and thermal shock accelerate seal aging, gradually reducing sealing force and reliability.
Solenoid valves typically use NBR, EPDM, FKM (Viton), or PTFE seals. Each material responds differently to heat, and incorrect selection can lead to premature failure.
| Sealing Material | Typical Temperature Range | Performance in High-Temperature Applications |
|---|---|---|
| NBR (Nitrile Rubber) | -10°C to 80°C | Hardens quickly at high temperature, loses elasticity, prone to early leakage |
| EPDM | -20°C to 150°C | Better resistance to steam and hot water, but gradually ages and loses sealing force under long-term heat |
| FKM (Viton) | -10°C to 200°C | Excellent heat and chemical resistance, stable sealing performance, higher material cost |
| PTFE (Teflon) | -20°C to 200°C+ | Outstanding thermal stability, minimal deformation, relies on structure rather than elasticity for sealing |
From field experience, using NBR seals in steam applications almost guarantees early leakage. Even EPDM seals will lose elasticity when exposed to near-limit temperatures for long periods.
Elastomer seals rely on elasticity to maintain contact pressure. At elevated temperatures, thermal expansion occurs, but molecular aging accelerates at the same time. Once elasticity decreases, micro-leakage paths form between the seal and valve core.
Thermal cycling worsens the problem. After cooling, aged seals cannot fully recover their original shape, leading to permanent deformation and ongoing leakage.
High temperatures also affect the clearance between the valve core and seat. Metal expansion may increase friction during operation, while cooling can enlarge gaps, further compromising sealing performance.
This explains why solenoid valves in hot water systems often energize correctly but fail to shut off completely.
As sealing friction changes, the force required to move the valve core also changes. In pilot operated solenoid valves, reduced sealing performance can disrupt pilot pressure balance, causing intermittent opening or closing failures.
Unstable operation is often an early indicator of seal degradation rather than an electrical fault.
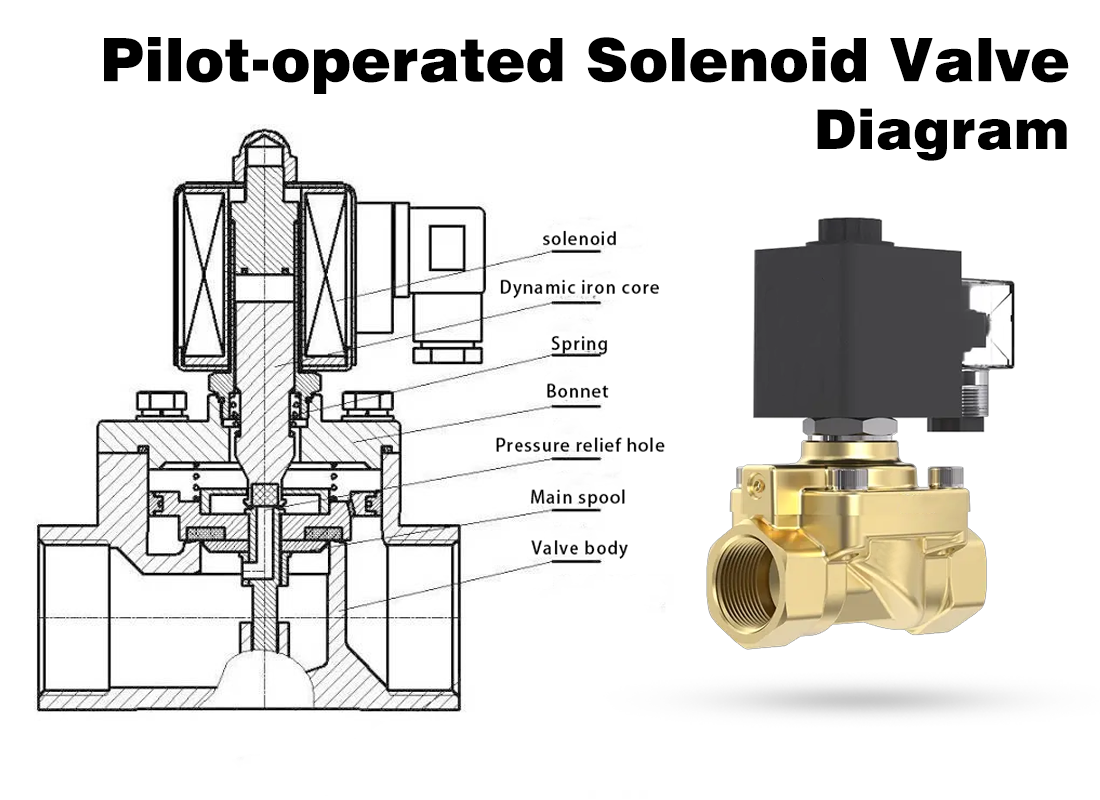
For high-temperature steam or hot water applications, solenoid valve selection should prioritize long-term sealing compatibility, not just maximum temperature ratings. PTFE seals or valves designed specifically for high-temperature service are often the safest choice.
For distributors and buyers, confirming continuous operating temperature and media type helps avoid costly replacements and system downtime.
(FK9025)
 How Diaphragm Material Affects Pulse Solenoid Valve Response Speed
How Diaphragm Material Affects Pulse Solenoid Valve Response Speed
 Effect of Diaphragm Aging on Pulse Solenoid Valve Blowing Performance
Effect of Diaphragm Aging on Pulse Solenoid Valve Blowing Performance
 Pulse Solenoid Valve Back-Blowing Interval and System Pressure Drop
Pulse Solenoid Valve Back-Blowing Interval and System Pressure Drop
 Instant High Flow Release: How Pulse Solenoid Valve Generates Strong Jet Intensity
Instant High Flow Release: How Pulse Solenoid Valve Generates Strong Jet Intensity
 Influence of Air Supply Pressure Fluctuation on Pneumatic Axial Valve Operation
Influence of Air Supply Pressure Fluctuation on Pneumatic Axial Valve Operation
You May Interest In






Dec 31, 2025 Blog
Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Manual Button Explained



FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap