Jan 23, 2026

In pneumatic and hydraulic systems, the 2-way solenoid valve is a fundamental control element, regulating fluid or air flow by moving its internal plunger. While often considered a generic component, the installation orientation—horizontal or vertical—directly affects plunger motion, switching stability, and overall system reliability. Understanding how gravity interacts with the plunger and comparing horizontal and vertical installation behaviors is essential for system designers, engineers, procurement specialists, and end users.
Whether dealing with a 2 way pneumatic solenoid valve or a 12 volt 2 way hydraulic solenoid valve, the plunger operates under a balance of spring force and electromagnetic force. When energized, the coil’s magnetic field pulls the plunger to open the valve; when de-energized, the spring pushes it back to close. Gravity, although often overlooked, plays a subtle yet critical role depending on the valve’s orientation:
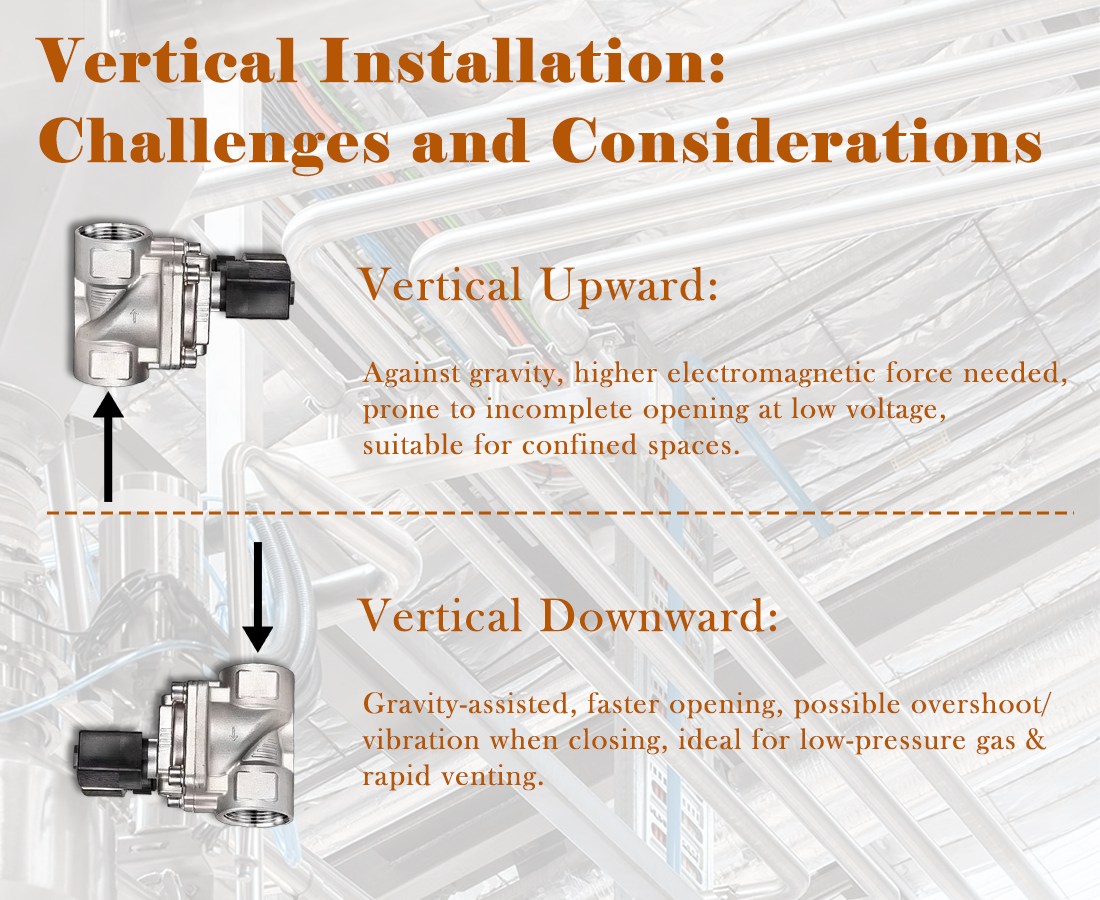
◆ Horizontal installation: Gravity acts perpendicular to plunger motion. Its effect is minimal, mainly introducing slight asymmetric friction along the guide sleeve.
◆ Vertical upward installation: Gravity resists plunger movement, requiring higher electromagnetic force for opening. Low-voltage scenarios, like 2 way air solenoid valve 12v applications, are most affected.
◆ Vertical downward installation: Gravity assists plunger motion, accelerating opening but potentially affecting closing dynamics.
For small-stroke valves like 2 way solenoid valves or low-voltage 2 way pneumatic solenoid valve, these gravitational effects can influence response time, operational consistency, and long-term durability.
| Installation Orientation | Gravity Effect on Plunger | Typical Impact on Operation |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal | Perpendicular to motion | Symmetric friction; high-frequency stability |
| Vertical Up | Opposes opening force | Slower opening; may require higher coil energy |
| Vertical Down | Assists opening force | Faster response; potential closing overshoot |
This table highlights how 2-way solenoid valves behave differently depending on mounting position. Horizontal installations generally provide more predictable and balanced plunger motion.

Horizontal orientation is often the default for pneumatic and low-pressure hydraulic applications:
• Plunger experiences symmetric forces, ensuring stable high-frequency operation.
• Minimizes bias wear, extending valve lifespan, especially in 2 way pneumatic solenoid valve 12v systems.
• Reduces micro-vibration or “chattering” during switching.
In automated assembly lines or air manifold control loops, horizontal mounting ensures 2 way solenoid valves respond predictably, maintaining throughput and reducing maintenance issues.
When the plunger moves upward against gravity:
• Requires more electromagnetic force to open.
• At low voltage or marginal supply conditions, the plunger may not fully open.
• Suitable for space-limited installations but demands attention to coil sizing and power supply.
With gravity assisting plunger motion:
• Opening is faster.
• May introduce overshoot or vibration during closing.
• Effective in low-pressure gas systems or applications needing rapid venting.
For 2-way solenoid valves, long-term vertical operation requires careful evaluation of opening/closing time, sticking risk, and wear accumulation. Proper plunger material and stroke design are essential to maintain reliability.
Valve switching consistency directly impacts control accuracy:
• Stable plunger movement ensures predictable system response.
• Prevents incomplete strokes or leakage, which can reduce performance.
• Reduces uneven wear, prolonging maintenance intervals.
Horizontal mounting typically yields the most uniform switching behavior, while vertical installation may need additional power or control adjustments to achieve similar stability.
For critical applications, selecting solenoid valve 2 way with orientation in mind prevents misfiring, pressure fluctuations, and energy inefficiency.
To optimize 2-way solenoid valve performance:
① Assess installation constraints: Determine if space allows horizontal or vertical mounting.
② Review manufacturer recommendations: Brands like ASCO 2 way solenoid valve provide guidance on orientation limits.
③ Validate during commissioning: Monitor response time and operational consistency to confirm installation choice.
Early attention to installation orientation reduces field adjustments and supports first-pass system reliability.
Installation orientation is more than a mechanical detail; it directly affects 2-way solenoid valve dynamics:
•Horizontal orientation generally offers symmetric plunger motion and predictable switching.
•Vertical orientation must consider gravity’s assistance or resistance.
•System voltage, valve type, and medium (air vs. hydraulic) all influence optimal orientation.
Understanding these factors helps engineers, distributors, and procurement specialists make informed design and selection decisions.
When specifying 2 way solenoid valves for pneumatic or hydraulic systems, careful consideration of installation direction ensures long-term reliability, stable operation, and minimal maintenance issues.
(FK9025)
 Fluid Retention During Supply and Exhaust Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
Fluid Retention During Supply and Exhaust Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
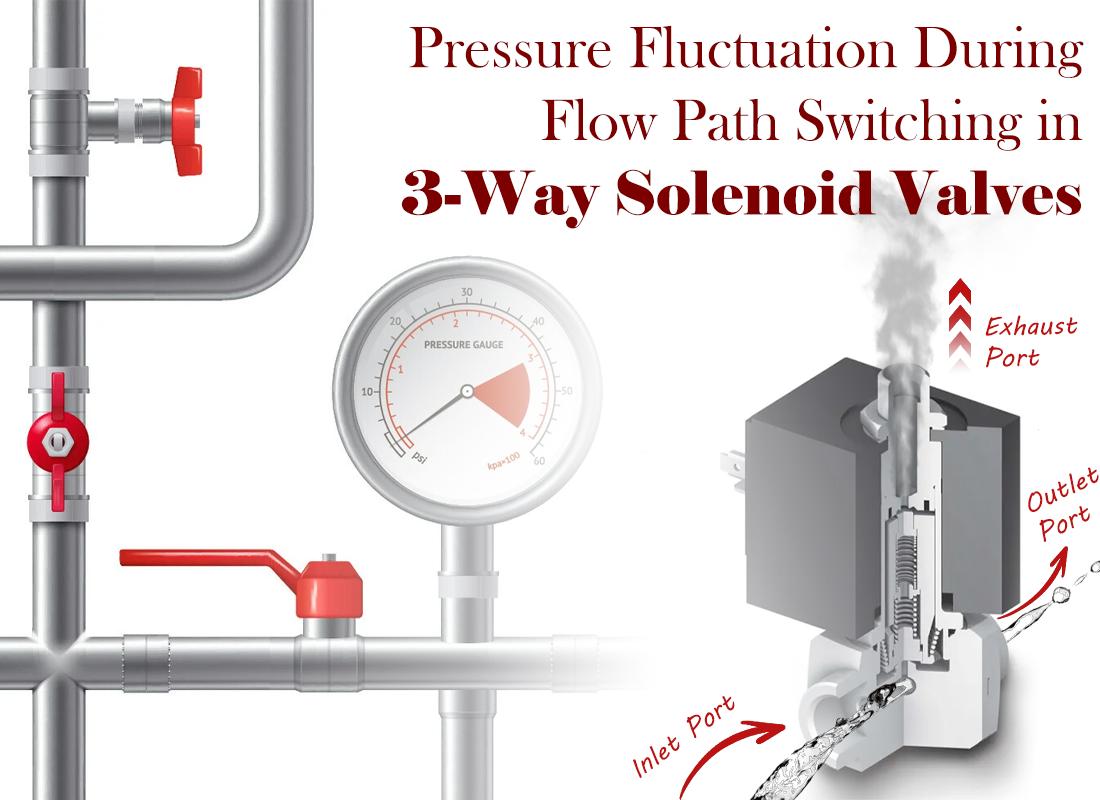 Pressure Fluctuation During Flow Path Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
Pressure Fluctuation During Flow Path Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
 Control Characteristics of 2-Way Solenoid Valves in Intermittent Liquid Supply Systems
Control Characteristics of 2-Way Solenoid Valves in Intermittent Liquid Supply Systems
 Impact of Contaminated Media on 2-Way Solenoid Valve Cores
Impact of Contaminated Media on 2-Way Solenoid Valve Cores
 2 Way Solenoid Valve Performance Differences in Gas and Liquid Media
2 Way Solenoid Valve Performance Differences in Gas and Liquid Media
You May Interest In
















Dec 31, 2025 Blog
Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Manual Button Explained




FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap