Jan 28, 2026

In many automated systems, fluid delivery is not continuous but controlled in repeated on-off cycles. These intermittent liquid supply systems are common in filling lines, dosing units, cleaning processes, and laboratory automation. Under such conditions, valve response time, repeatability, and stability become more critical than nominal flow ratings. The 2-way solenoid valve is widely used in these applications, but its advantages and limitations must be clearly understood.
Intermittent supply requires valves to open and close within short cycles while maintaining consistent performance. Any delay in actuation or incomplete sealing directly affects dosing accuracy. Compared with proportional devices, 2-way solenoid valves offer a direct on-off mechanism, making them well suited for short-cycle control in many industrial solenoid valve applications.
Structurally, a solenoid valve 2 way has a simple flow path and a short moving stroke. When energized, the electromagnetic force acts directly on the plunger, enabling fast response with minimal mechanical inertia. This makes the normally closed solenoid valve configuration particularly effective for intermittent dosing, where power-off sealing also improves system safety.
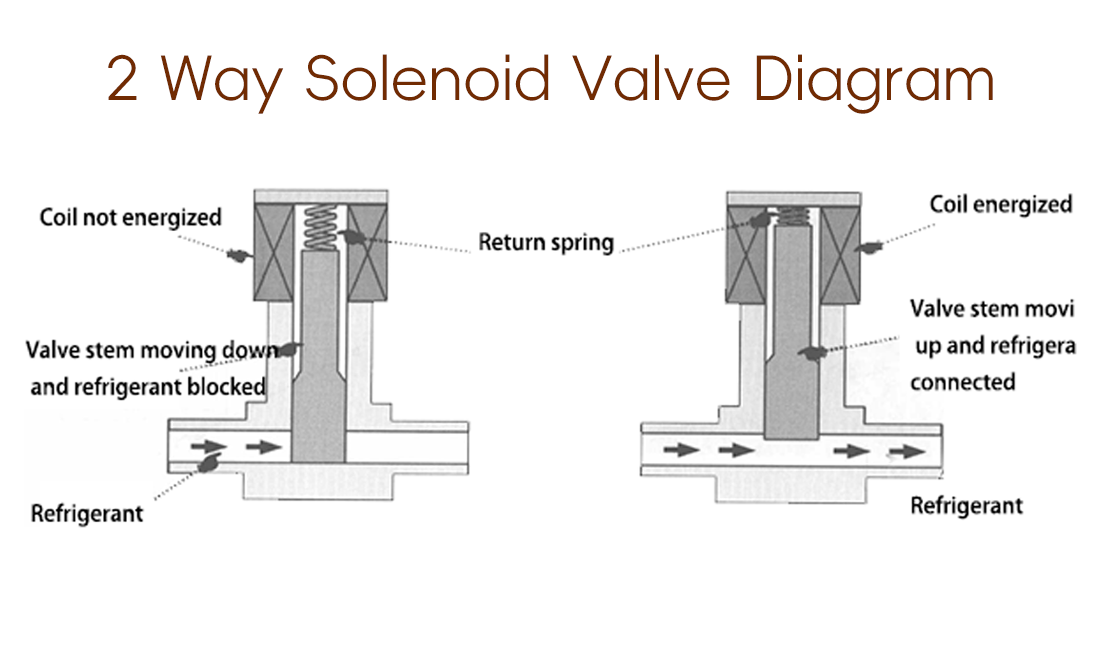
For pneumatic and low-pressure liquid systems, the 2-way solenoid valve provides reliable switching with relatively low energy consumption, even under frequent actuation.
Fast response alone does not guarantee system stability. In liquid systems, frequent switching can cause pressure fluctuations that act back on the valve core, affecting closing speed and repeatability. In high-frequency duty cycles, coil heating becomes a critical factor, as excessive temperature rise can reduce magnetic force and alter valve performance.
These limitations highlight why 2-way solenoid valves must be selected based on real operating cycles, not just catalog specifications.
| Control Condition | Valve Behavior | Design Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Short cycle, low flow | Fast response, stable cut-off | Focus on coil cooling |
| Short cycle, liquid media | Sensitive to pressure fluctuation | Optimize piping layout |
| High-frequency switching | Increased thermal load | Select high-duty cycle coil |
| Precise dosing | Repeatable opening time | Normally closed structure preferred |
For short-cycle, low-flow applications, standard 2-way solenoid valves are usually sufficient. However, as switching frequency increases, engineers should evaluate coil duty rating, thermal dissipation, and piping design. In demanding applications, optimizing these factors ensures stable operation and extends valve service life.
(FK9025)
 Fluid Retention During Supply and Exhaust Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
Fluid Retention During Supply and Exhaust Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
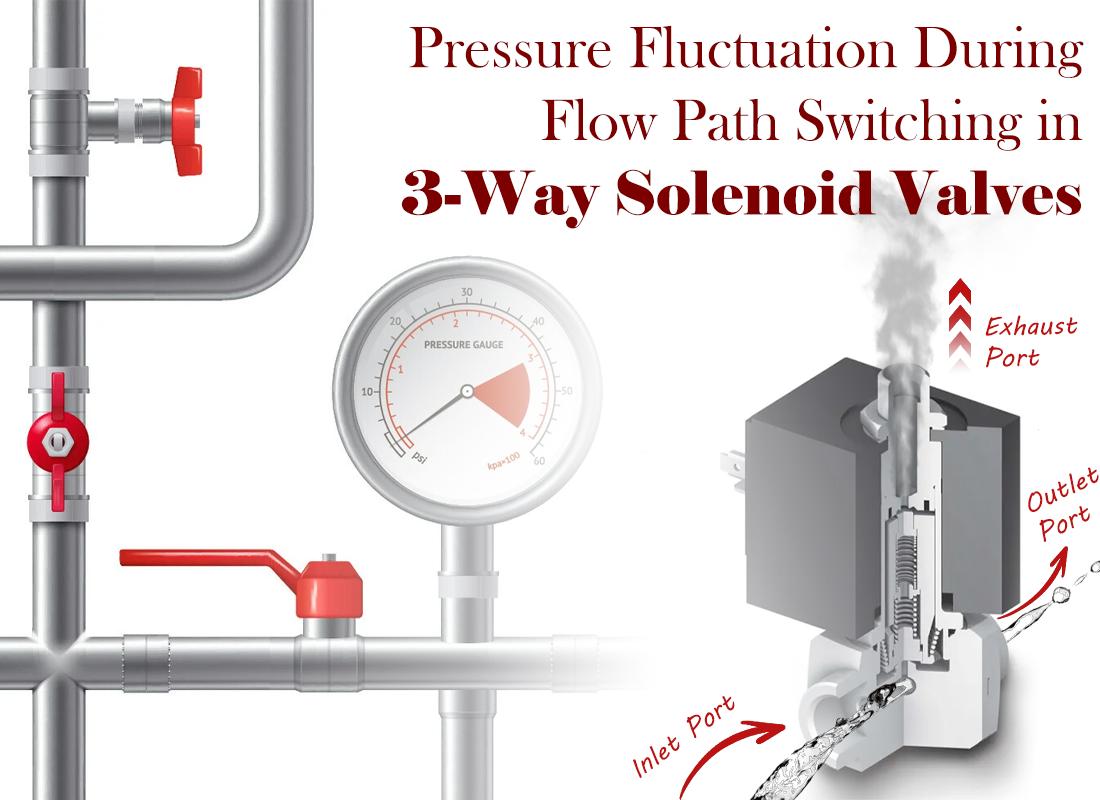 Pressure Fluctuation During Flow Path Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
Pressure Fluctuation During Flow Path Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
 Control Characteristics of 2-Way Solenoid Valves in Intermittent Liquid Supply Systems
Control Characteristics of 2-Way Solenoid Valves in Intermittent Liquid Supply Systems
 Impact of Contaminated Media on 2-Way Solenoid Valve Cores
Impact of Contaminated Media on 2-Way Solenoid Valve Cores
 2 Way Solenoid Valve Performance Differences in Gas and Liquid Media
2 Way Solenoid Valve Performance Differences in Gas and Liquid Media
You May Interest In



















Dec 31, 2025 Blog
Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Manual Button Explained




FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap