Jan 22, 2026

In automated control systems, 2 way solenoid valves are widely used for periodic on/off control such as dosing, pulsed water supply, or timed cleaning processes. While the control logic appears simple, long-term operation often reveals vibration, noise, or premature sealing failure within the piping system.
These issues are rarely caused by poor valve quality. Instead, they result from repeated interruption and release of fluid flow.
In steady-flow pipelines, pressure and velocity remain relatively stable. However, in cyclic control systems, fluid is repeatedly stopped and released. Each rapid closure and opening introduces a pressure disturbance into the system.
At low switching frequency, the system can absorb these fluctuations. As frequency increases, pressure waves begin to overlap, gradually turning into noticeable vibration and noise.
A 2 way solenoid valve is fundamentally an on/off device. The valve core moves rapidly between fully closed and fully open positions, without intermediate buffering.
This instantaneous action causes sudden changes in flow velocity. According to fluid dynamics principles, the faster the velocity change, the stronger the resulting pressure impact. In high-frequency operation, this impact is continuously repeated.
In real installations, engineers often observe:
◆ Audible knocking sounds during valve actuation
◆ Slight pipe movement at supports
◆ Pressure gauge needle oscillation
◆ Reduced seal and seat lifespan
These symptoms can occur even when operating within rated pressure and flow limits, because they are related to dynamic pressure behavior, not static ratings.
When switching frequency increases, pressure waves from previous cycles may not fully dissipate before the next event occurs. As a result, pressure fluctuations accumulate rather than reset.
The fast response of a 2 way solenoid valve, normally an advantage, becomes a factor that amplifies pressure instability under these conditions.
| Control Method | Valve Behavior | Impact Risk | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| On/Off solenoid valve | Instant switching | High | Dosing systems |
| Modulating valve | Gradual movement | Low | Flow regulation |
| Pilot-assisted valve | Damped motion | Medium | General automation |
For engineers and buyers, it is important to evaluate whether direct on/off control is appropriate for a given application. Common mitigation strategies include reducing switching frequency, adding buffering volume, or selecting valve designs with damped movement.
Understanding how fluid reacts to rapid interruption is essential for making reliable valve selections.
(FK9025)
 Fluid Retention During Supply and Exhaust Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
Fluid Retention During Supply and Exhaust Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
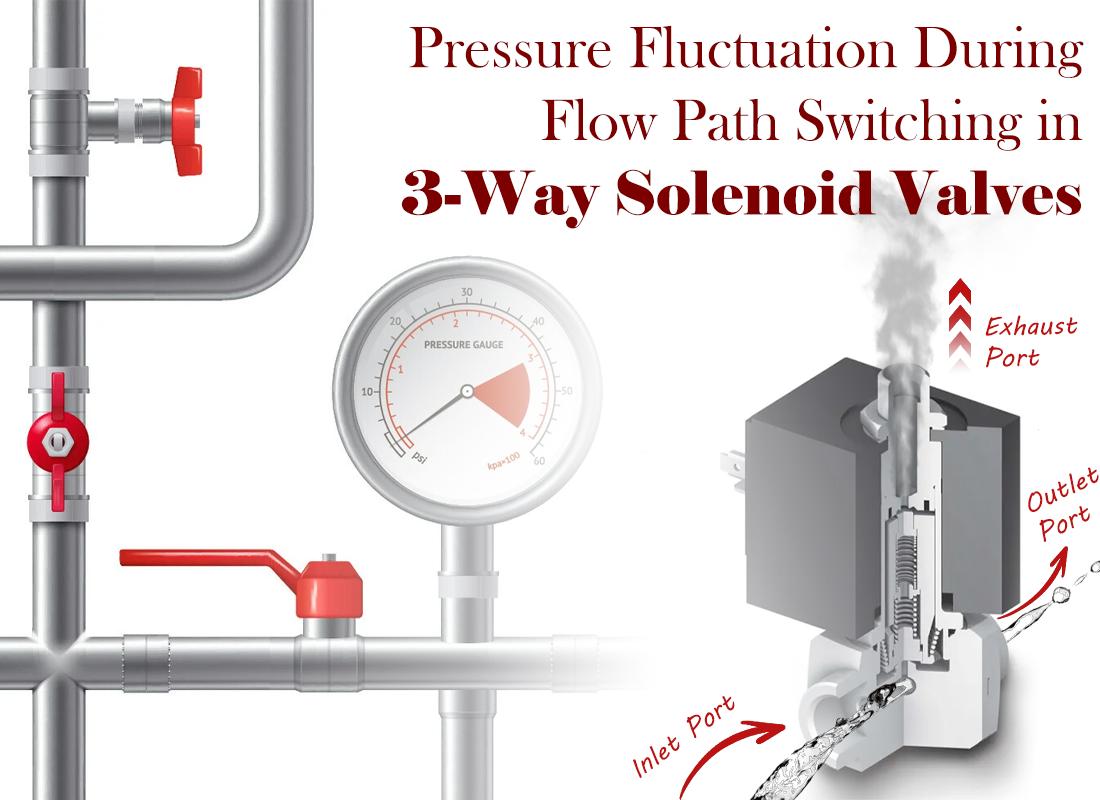 Pressure Fluctuation During Flow Path Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
Pressure Fluctuation During Flow Path Switching in 3-Way Solenoid Valves
 Control Characteristics of 2-Way Solenoid Valves in Intermittent Liquid Supply Systems
Control Characteristics of 2-Way Solenoid Valves in Intermittent Liquid Supply Systems
 Impact of Contaminated Media on 2-Way Solenoid Valve Cores
Impact of Contaminated Media on 2-Way Solenoid Valve Cores
 2 Way Solenoid Valve Performance Differences in Gas and Liquid Media
2 Way Solenoid Valve Performance Differences in Gas and Liquid Media
You May Interest In














Dec 31, 2025 Blog
Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Manual Button Explained




FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap